Field Test
Services
Field Test
Field testing in the construction industry involves on-site assessments to evaluate the performance, strength, and integrity of various elements. Here are descriptions for some common field tests:
Pile Load Test
Non - Destructive Testing
Plate Load Test
Dynamic Load Testing
Concrete Core Testing
Cross - Hole Sonic Logging (CSL)
Services
Field Test
Field testing in the construction industry involves on-site assessments to evaluate the performance, strength, and integrity of various elements. Here are descriptions for some common field tests:

Pile Load Test

Non - Destructive Testing
Plate Load Test


Dynamic Load Testing
Concrete Core Testing
Cross - Hole Sonic Logging (CSL)
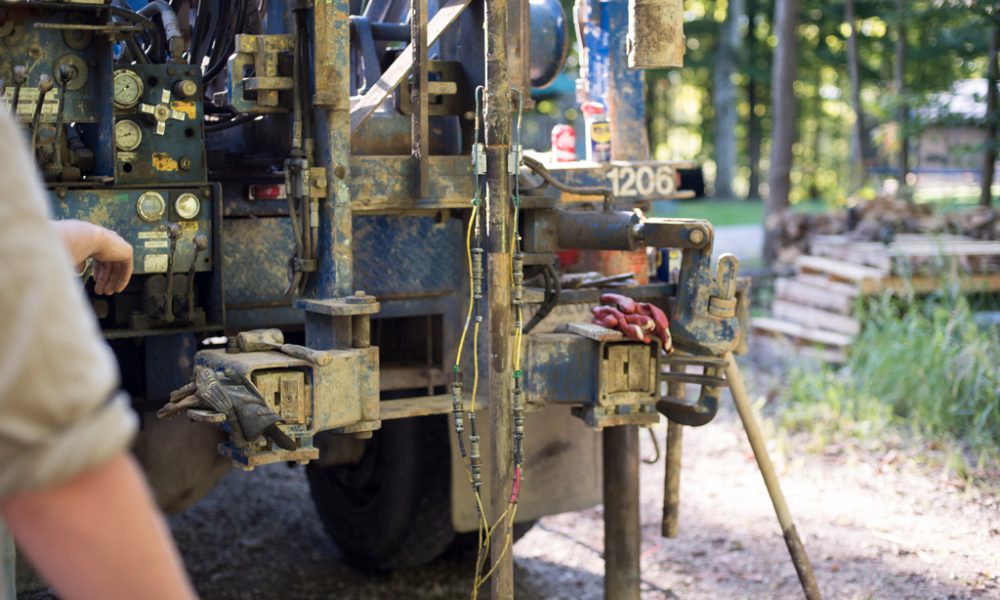
Standard Penetration Test (SPT)
Standard Penetration Test (SPT) is a simple and low-cost testing procedure widely used in geotechnical investigation to determine the relative density and angle of shearing resistance of cohesionless soils and also the strength of stiff cohesive soils.

Modulus Of Subgrade Reaction (K - Value)
Relation of load, deflection and modulus of subgrade reaction (k). The value of k is in terms of MPa/m (pounds per square inch per inch of deflection, or pounds per cubic inch – pci) and ranges from about 13.5 MPa/m (50 pci) for weak support, to over 270 MPa/m (1000 pci) for strong support.


Earth Resistivity Test
Soil resistivity testing is the process of measuring a volume of soil to determine the conductivity of the soil. The resulting soil resistivity is expressed in ohm-meter or ohm-centimeter. Soil resistivity testing is the single most critical factor in electrical grounding design.
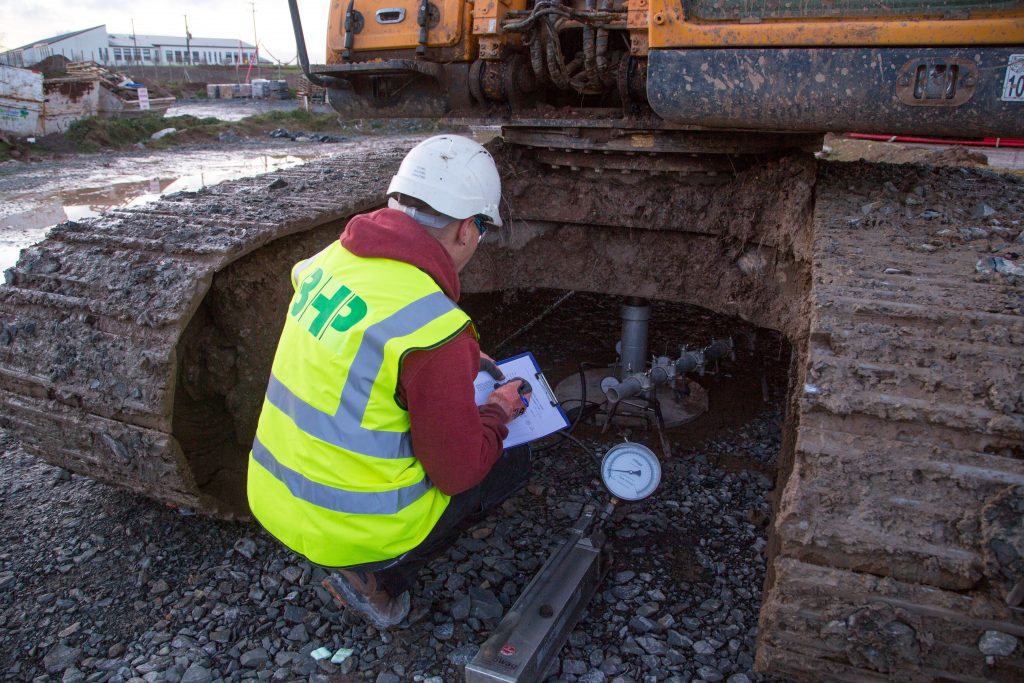
Field CBR Test
The California Bearing Ratio (CBR) field test measures the relative strength of in–situ soils and some base course materials for use in pavement design. The field test procedure uses a loading jack to force a piston into the soil at the test site and comparing the piston load to the depth of penetration.


Single And Double Packer Test (Field Permeability Test)
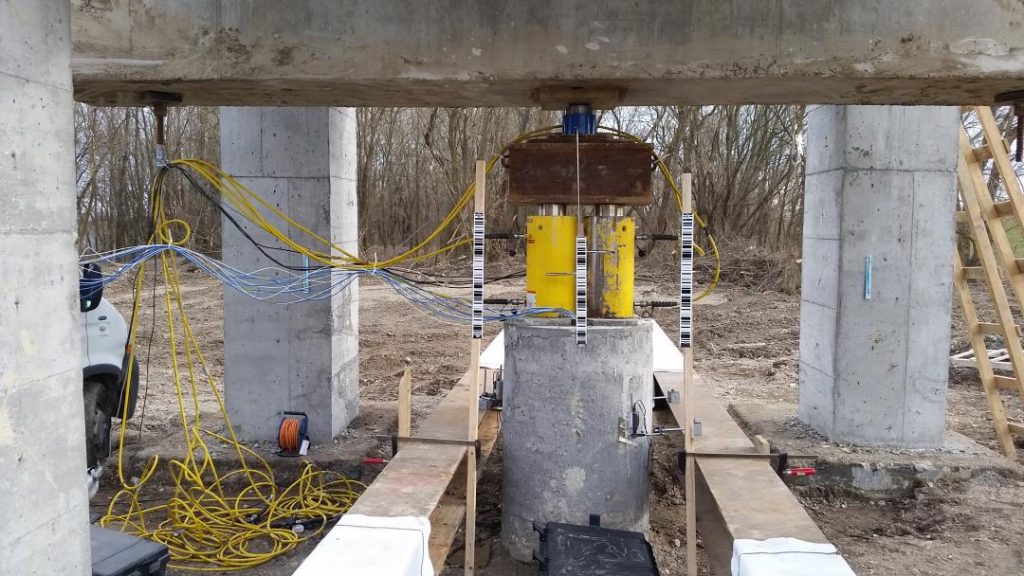
Pile Load Test
Pile Load Testing is performed to assess the load-carrying capacity of deep foundations, such as piles or drilled shafts. The test involves applying a known load to the pile and monitoring the resulting settlement. Pile Load Tests help verify the design assumptions, evaluate pile performance, and ensure that the foundation can support the intended loads.
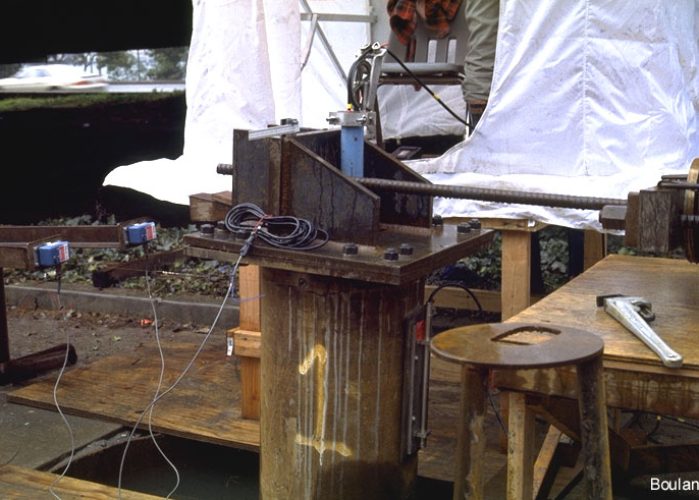


Pile Lateral Test
This test method covers procedures for testing vertical. and batter piles either individually or in groups to. determine the load-deflection relationship when. subjected to lateral loading.Lateral capacity of these piles depends on the properties of soil. Pile behaves as a transversely loaded beam in case of lateral loads and they transfer lateral load to surrounding soil by means of lateral resistance of the soil.
Pile Pullout Test
The pullout tests were conducted to determine the tension capacity of a pile and to assess the effects of lateral loading on pullout resistance. The safe load shall be the least of the following: 2/3rd of the load at which the total displacement is 12 mm or the load corresponding to a specified permissible lift.
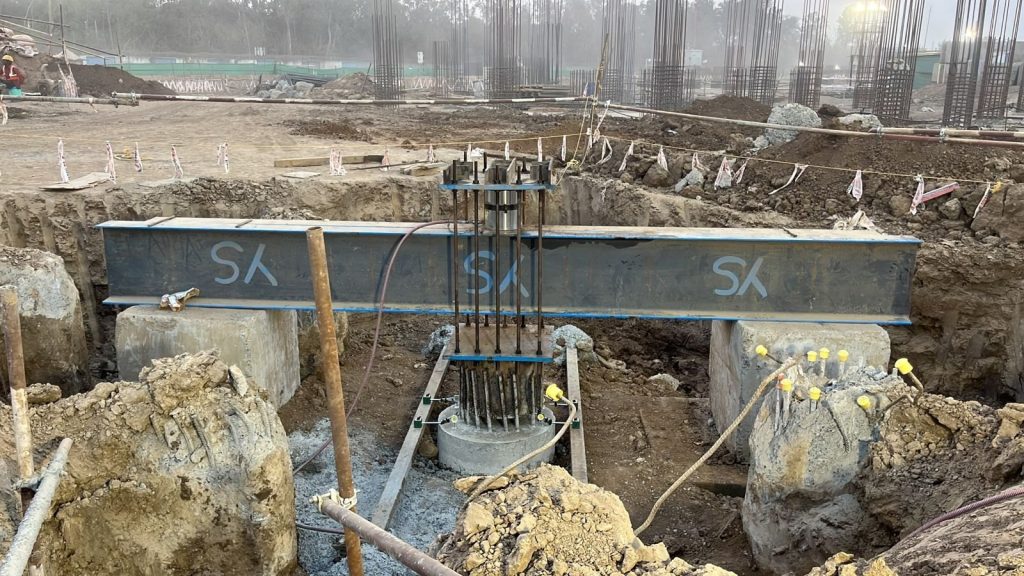
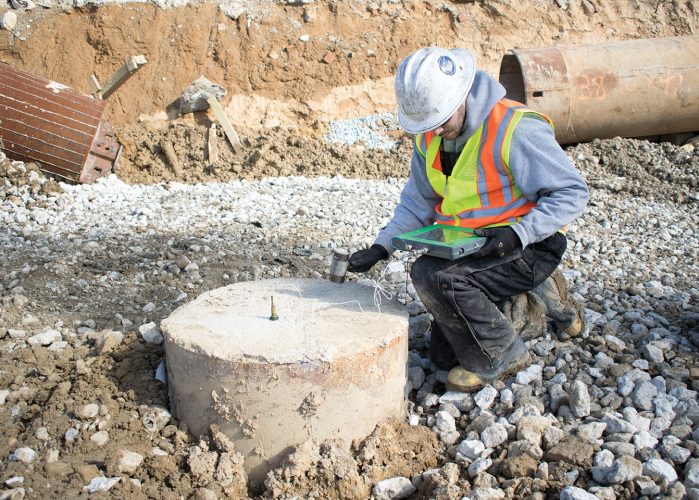


Pile Integrity Test
Pile Integrity Test (PIT), or “low strain impact integrity testing of deep foundation” is a widely used non-destructive test method for the evaluation of pile quality, and integrity. The test can also be used to estimate the unknown length of existing piles and foundations.
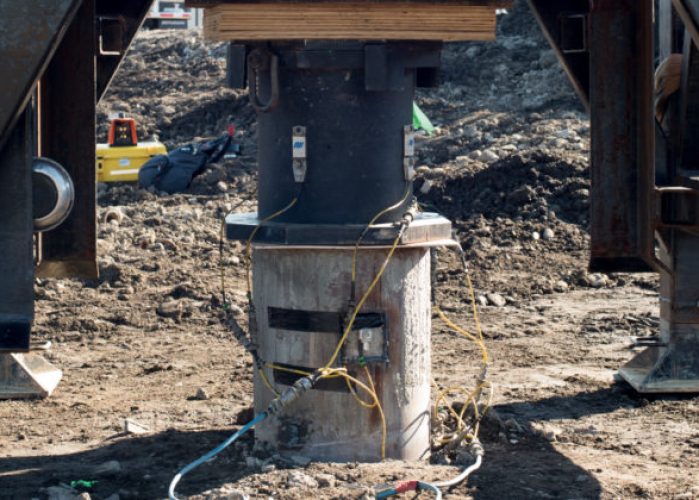

Dynamic Load Testing
Dynamic Load Testing involves applying dynamic loads to a foundation element, such as a pile, and measuring the response. This test helps assess the capacity, integrity, and dynamic characteristics of foundations. Dynamic Load Testing is particularly useful for deep foundations in areas with challenging soil conditions.
Non - Destructive - Rebound Hammer Test
Non-destructive testing is a group of techniques used to assess the properties of materials and structures without causing damage. In construction, NDT methods include ultrasonic testing, Rebound hammer testing, Half-cell potentiometer tests. These tests are valuable for evaluating the condition of existing structures, detecting flaws, and ensuring the safety and reliability of structure. The Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity Test is a non- destructive method used to assess the quality and integrity of concrete structures. It measures the speed of ultrasonic pulses through the material, helping identify voids, cracks, or other anomalies. This test is valuable for evaluating the structural health of concrete elements.
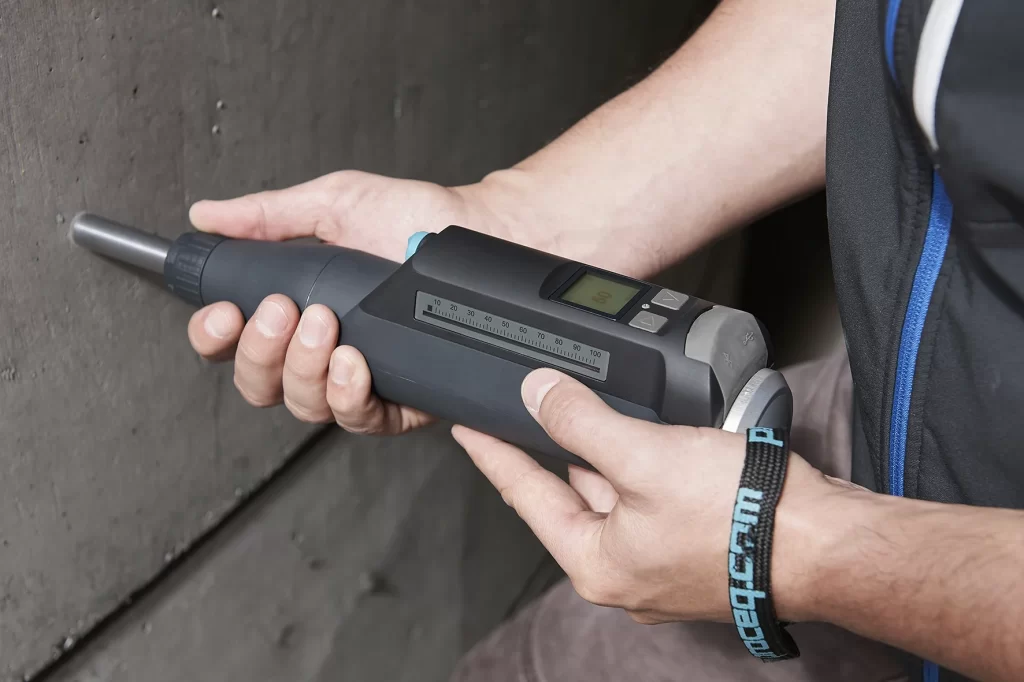


Ultra - Sonic Pulse Velocity Test
Ultrasonic pulse velocity (UPV) test is a nondestructive popular test used to examine the homogeneity, quality, cracks, cavities, and defects in concrete.access is generally available to opposite surfaces of a test specimen. and ultrasonic tests are commonly conducted using direct transmission. Direct transmission is defined as the propagation of ultrasonic stress waves along a straight-line path between the opposite surfaces of a speci men.
Half Cell Potential Test
The half-cell potential test is the only corrosion monitoring technique standardized in ASTM C876 – 15: Standard Test Method for Corrosion Potentials of Uncoated Reinforcing Steel in Concrete. It is used to determine the probability of corrosion within the rebar in reinforced concrete structures.
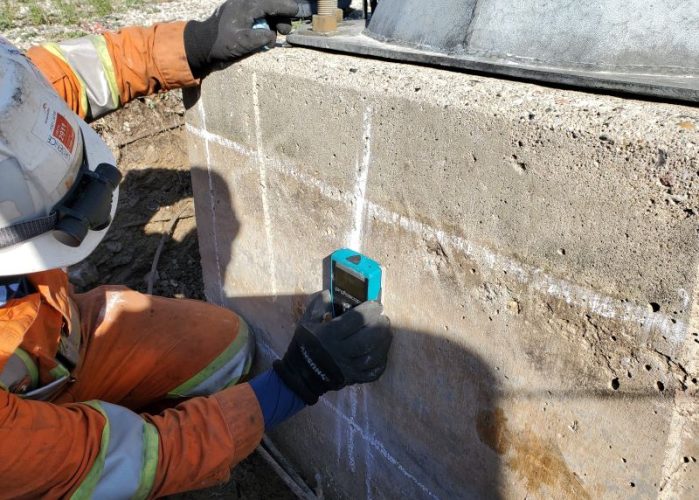


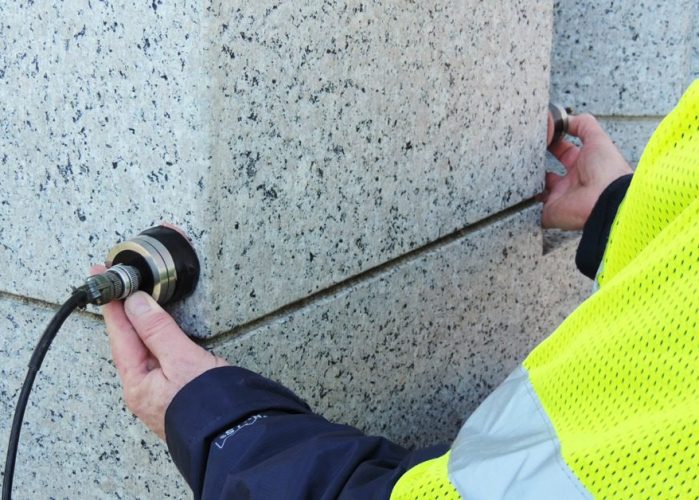
Cover Depth Test
Concrete cover measurement is performed by using various non destructive tests such as GPS (ground penetrating radar), electromagnetic test, ultrasonic and radiography. The most popular test is using electromagnetic energy such as ground penetrating radar equipments.
Block Vibration Test
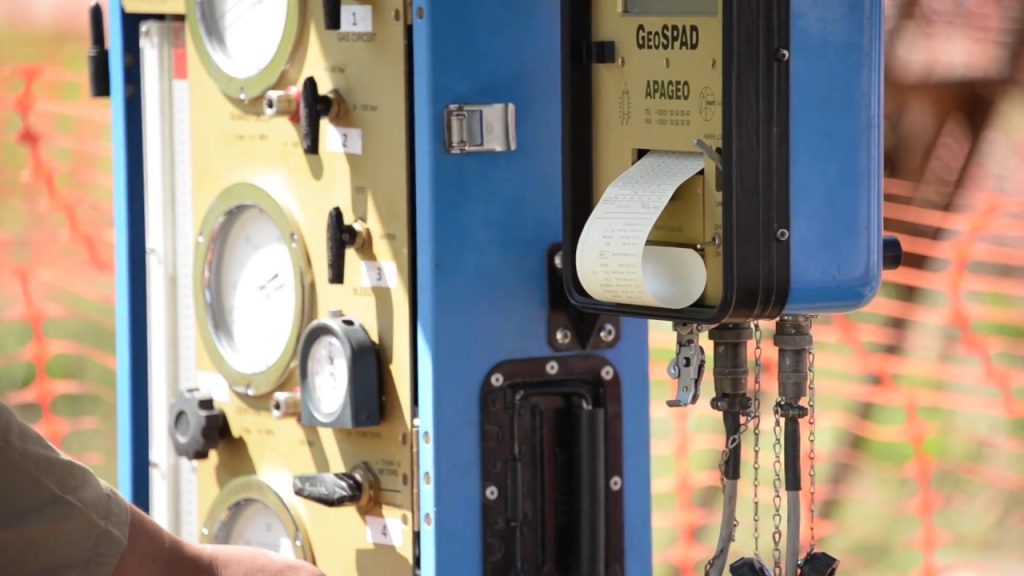


Benkelman Beam Deflection
The Benkelman Beam is used with a loaded truck – typically 80 kN (18,000 lb) on a single axle with dual tires inflated to 480 to 550 kPa (70 to 80 psi). Measurement is made by placing the tip of the beam between the dual tires and measuring the pavement surface rebound as the truck is moved away
Falling Weight Deflectometer (FWD) Testing
The Falling Weight Deflectometer (FWD) is a device that is used to evaluate pavement and pavement layer stiffness. It is a trailer-mounted device that operates by dropping a weight on to the pavement and measuring the resulting pavement deflections.
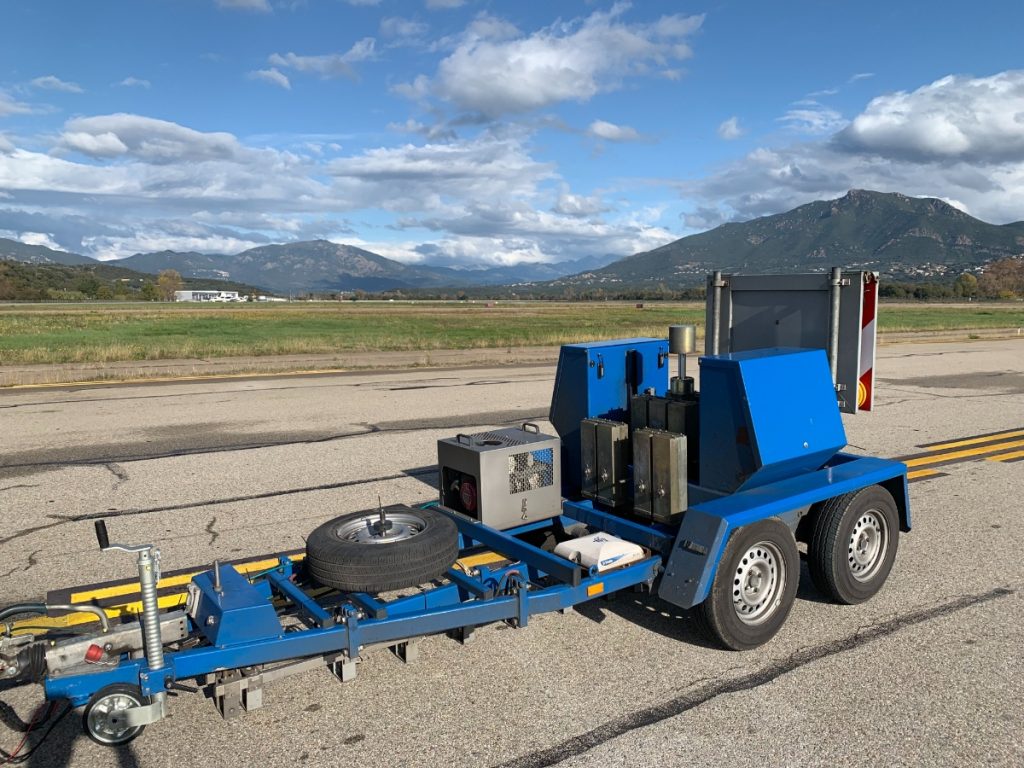
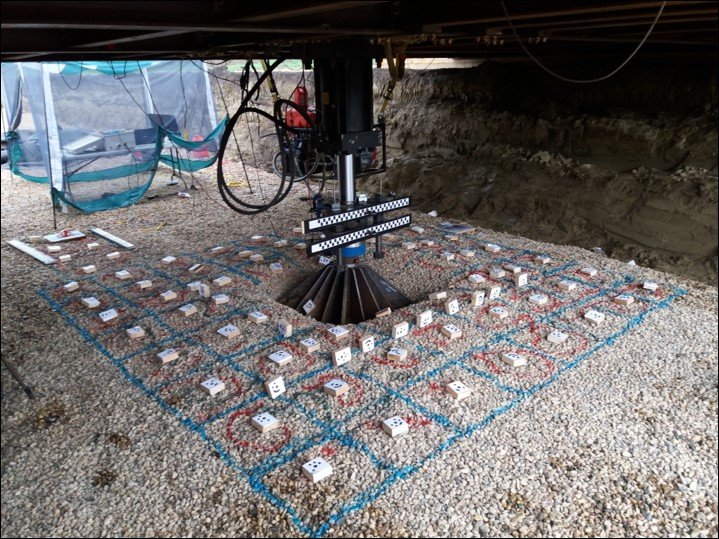


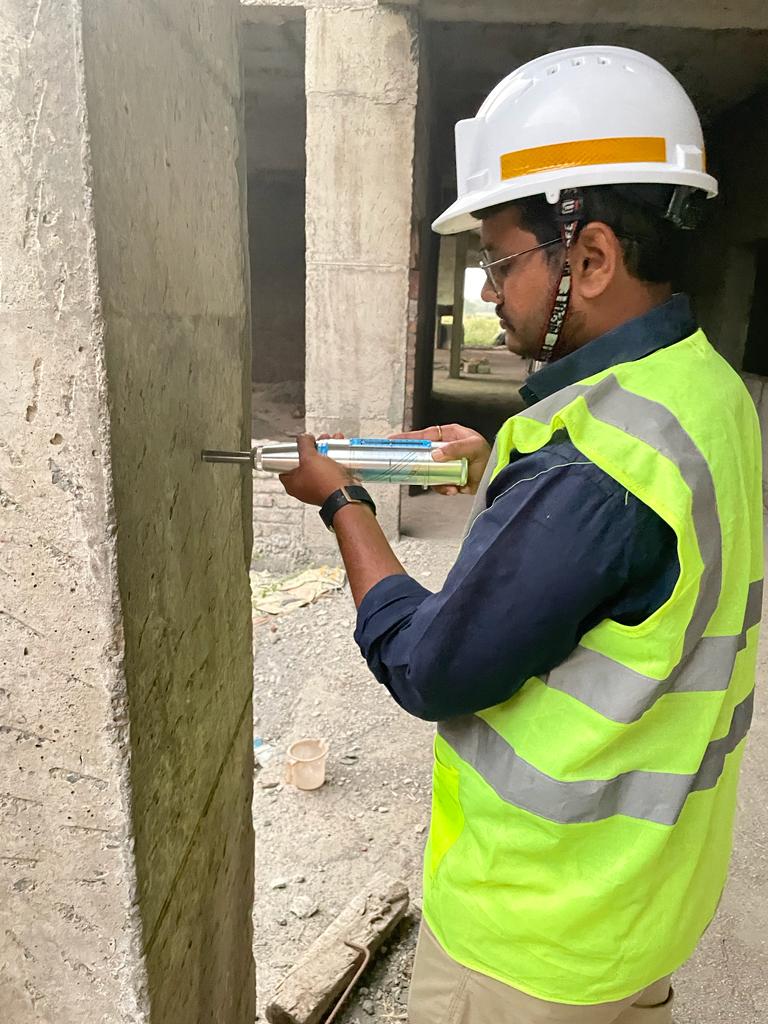
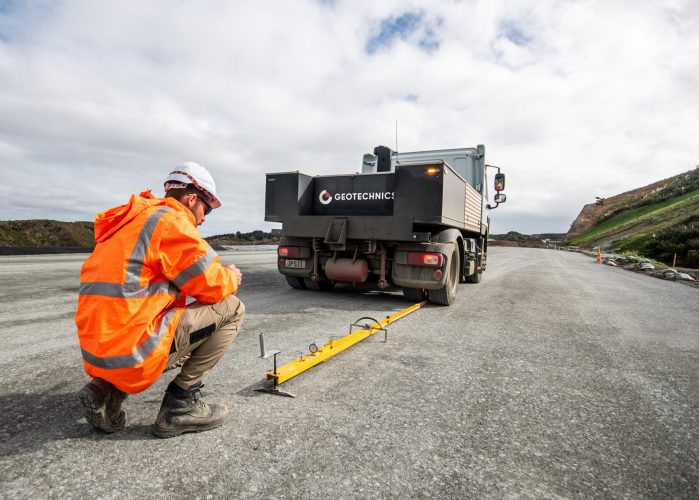
Plate Load Test
The Plate Load Test is conducted to determine the bearing capacity of soil, especially for foundation design. A steel plate of known diameter is placed on the ground, and a load is gradually applied. The settlement of the plate is measured at various load levels. This test helps engineers understand the soil’s load-bearing capacity and its ability to support structures.
Concrete Core Testing
Concrete Core Testing is conducted by extracting cylindrical cores from hardened concrete structures. These cores are then tested to evaluate compressive strength, assess the quality of concrete, and identify any defects or deterioration. This information is essential for assessing the structural integrity of existing concrete elements.
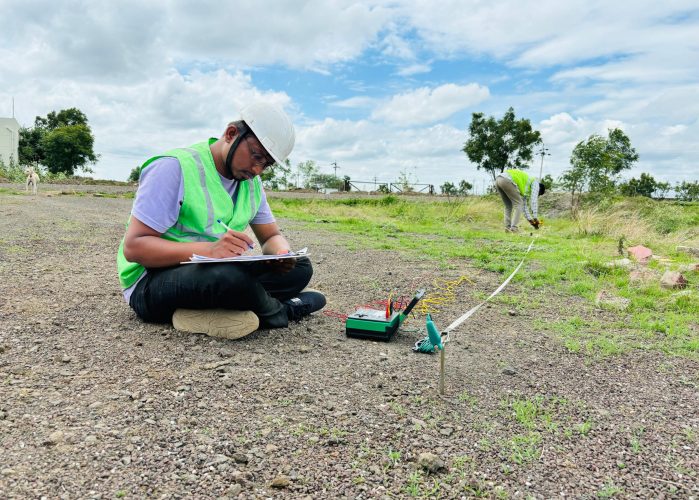


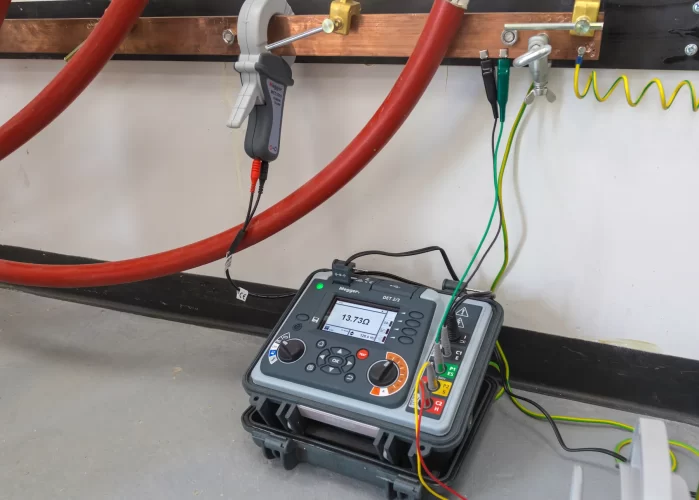
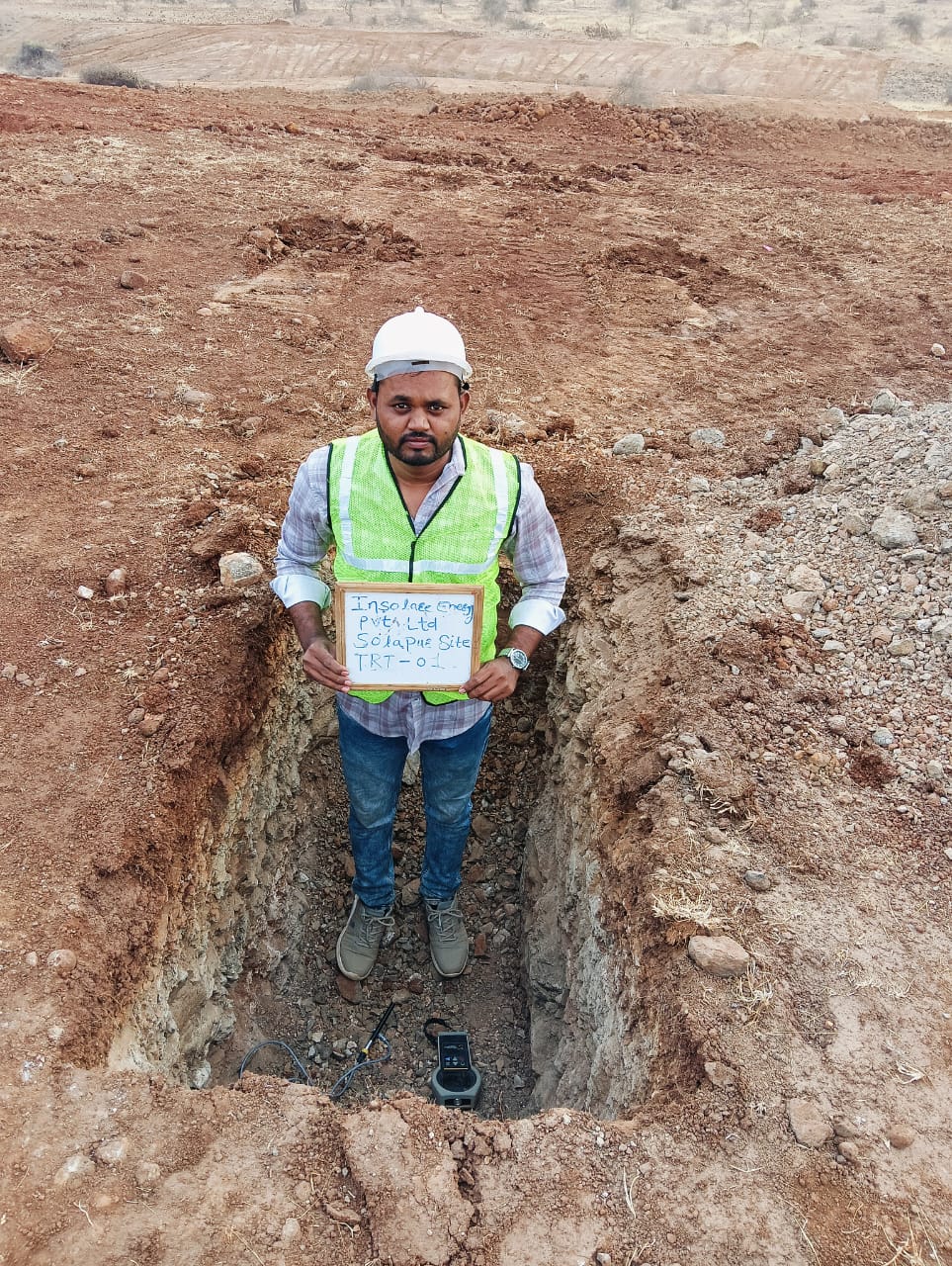
Earth Resistivity Test (ERT)
Earth Resistivity Test is a non-destructive test used to evaluate the sub-surface soil’s ability to conduct electricity, which is crucial for designing effective earthing systems. It involves the use of electrodes placed in the ground to measure the resistance of soil to the flow of electrical current. This test helps determine the most suitable location and depth for grounding systems and identifies variations in soil composition, moisture content, and other factors affecting resistivity.
Thermal Resistivity Test
Thermal Resistivity Test is a non-destructive test used to measure the soil’s resistance to heat flow, which is essential in the design and installation of underground power cables and thermal backfill materials. It involves applying heat to a probe buried in the soil and measuring the temperature rise over time. This test helps determine the soil’s ability to dissipate heat and ensures safe and efficient thermal performance of buried electrical systems.

Field Tests

Pile Load Test evaluates the load-carrying capacity of deep foundations like piles or drilled shafts. A known load is applied, and settlement is measured to verify design assumptions, assess performance, and ensure the foundation can safely support the intended loads.
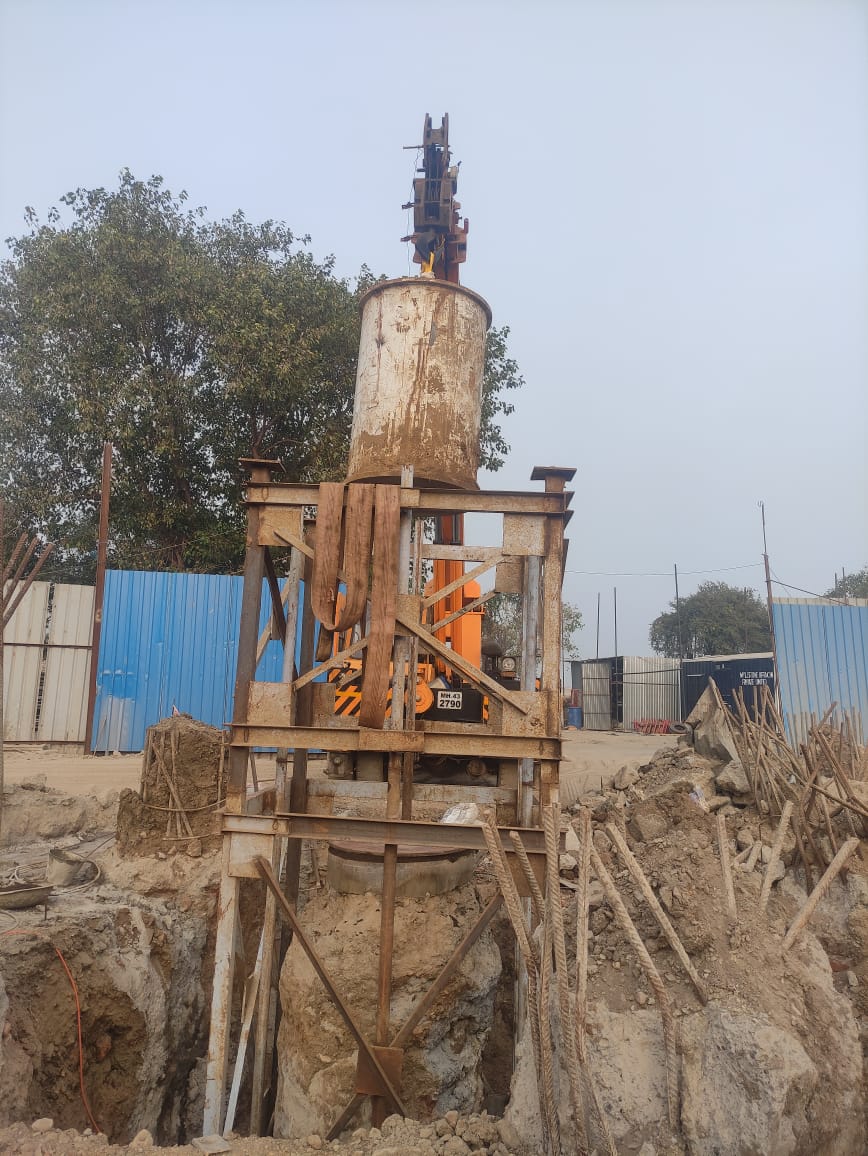

Dynamic Load Testing assesses the capacity and integrity of foundation elements by applying dynamic loads and measuring the response. It is especially useful for evaluating deep foundations in challenging soil conditions.

NDT refers to techniques used to evaluate materials and structures without causing damage.In construction,common NDT methods include ultrasonic testing, rebound hammer testing, and half-cell potentiometer testing.
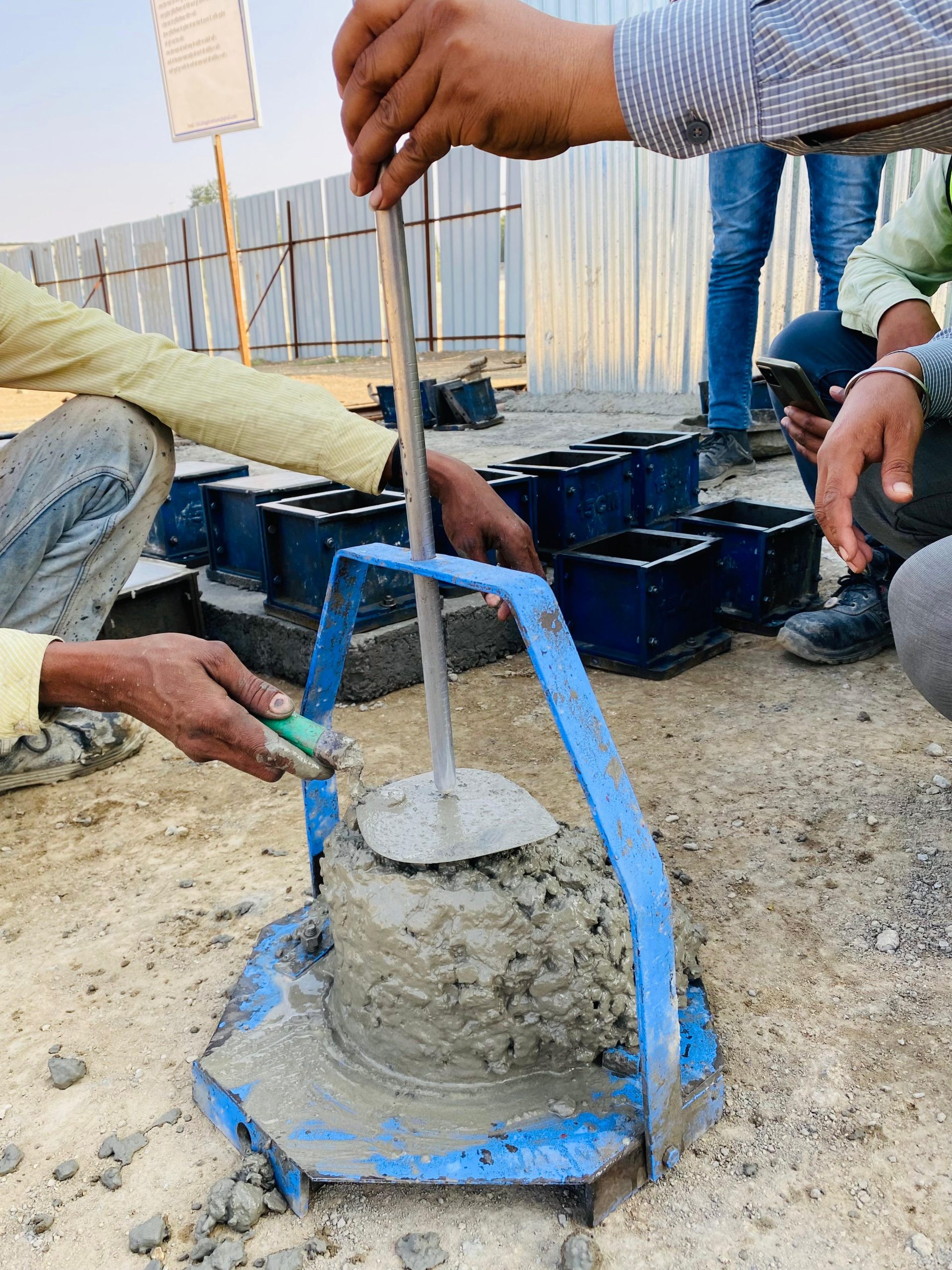

Concrete Core Testing involves extracting cylindrical samples from hardened concrete to assess compressive strength, quality, and potential defects. It provides critical data for evaluating the structural integrity of existing concrete elements.
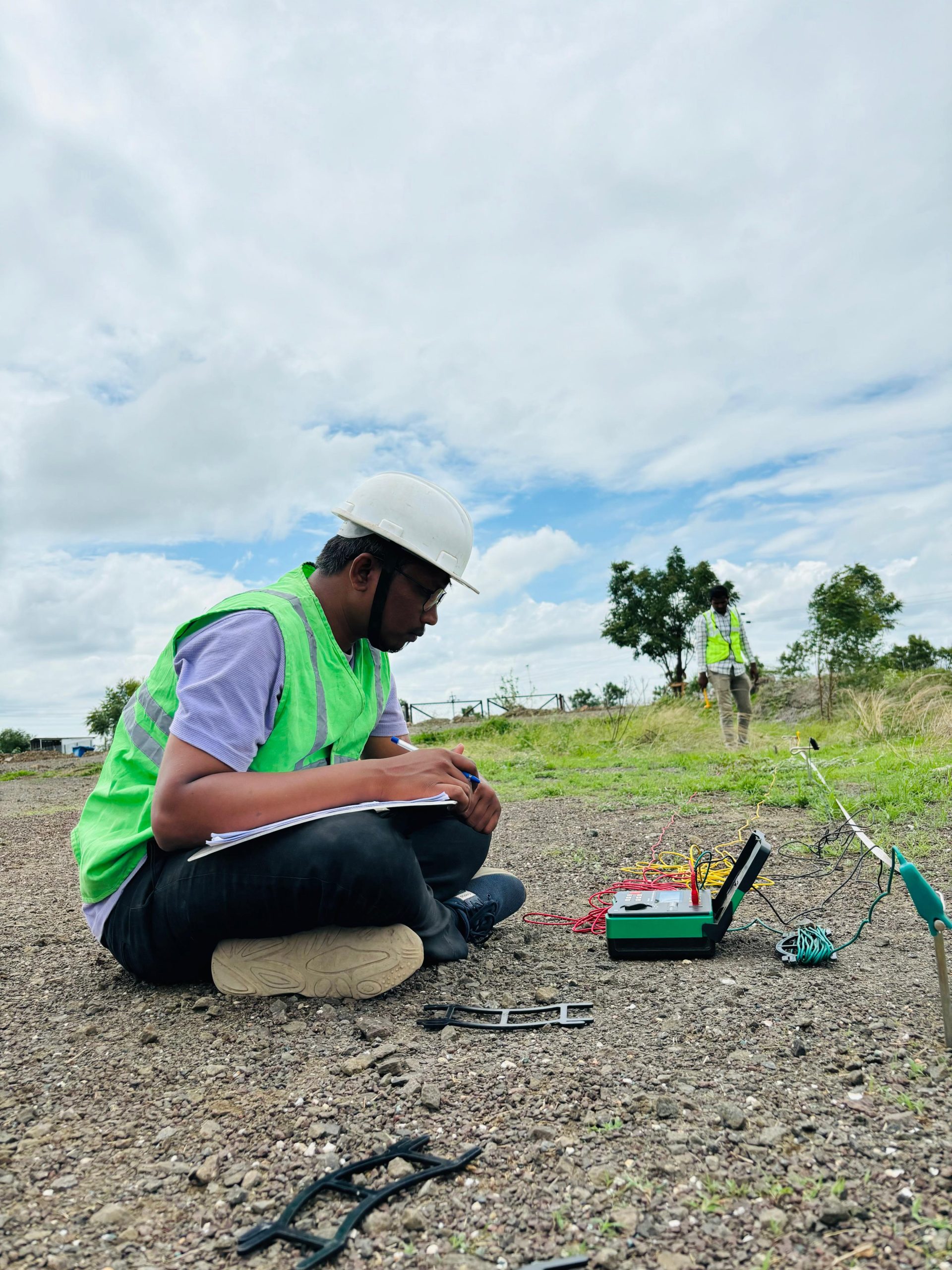

Earth Resistivity Test is a non-destructive method used to evaluate soil’s electrical conductivity. Electrodes are placed in the ground to measure resistance, helping determine suitable grounding system locations and identify changes in soil composition and moisture.
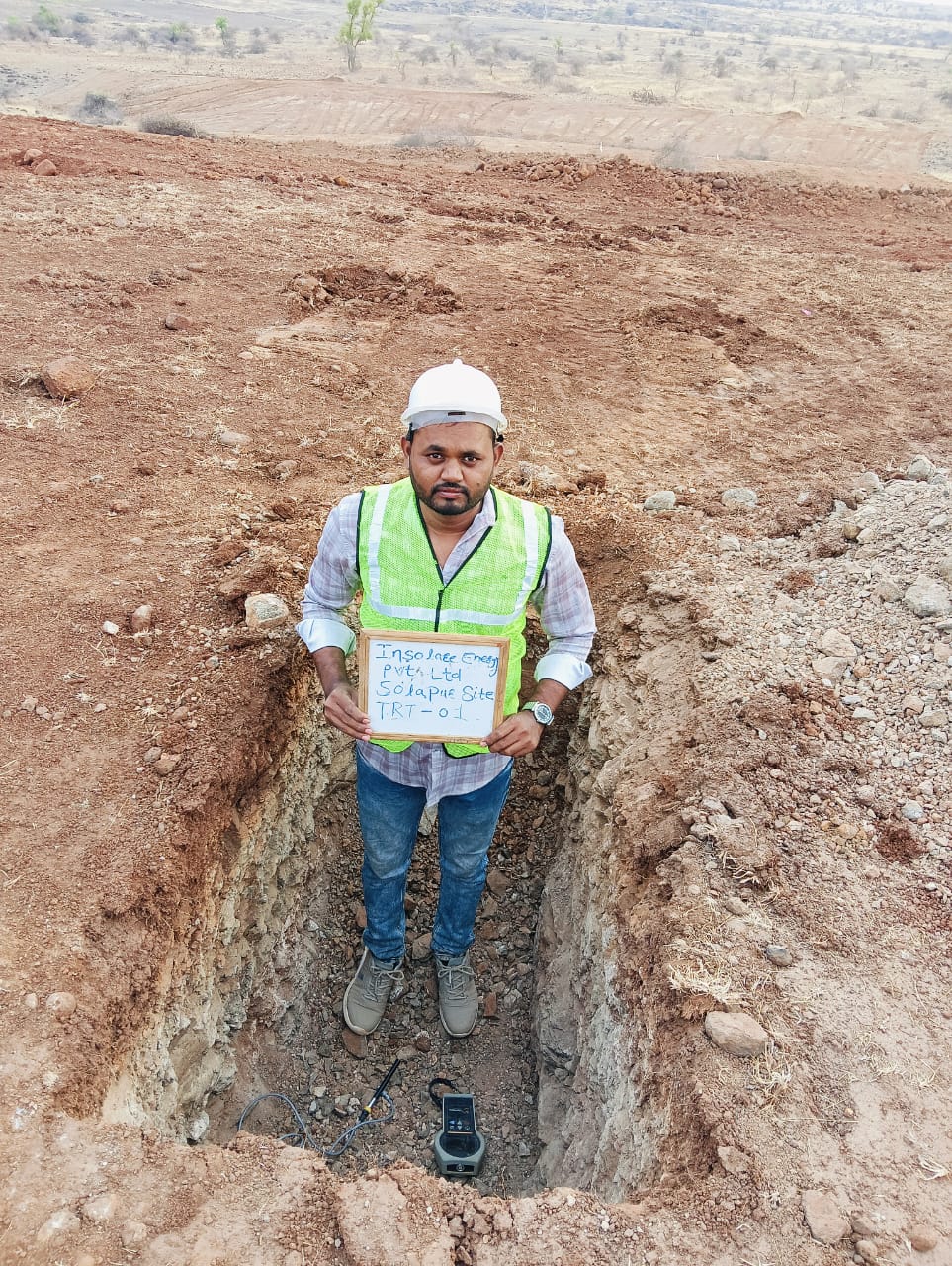

Thermal Resistivity Test is a non-destructive method used to measure soil’s resistance to heat flow. By heating a buried probe and tracking temperature rise, it assesses the soil's ability to dissipate heat—critical for designing safe and efficient underground cable systems.

Plate Load Test determines the soil's bearing capacity for foundation design. A known-size steel plate is loaded gradually, and the resulting settlements are measured to assess the soil's ability to support structural loads. .
