Laboratory Test
Services
Laboratory Test
Laboratory testing of soil, cement, aggregates, construction materials, and water is a critical component of civil engineering to ensure the quality, durability, and safety of infrastructure projects. Here are descriptions for each type of laboratory testing:
Cement Testing
Aggregate Testing
Water Testing
Soil Testing
Concrete Testing
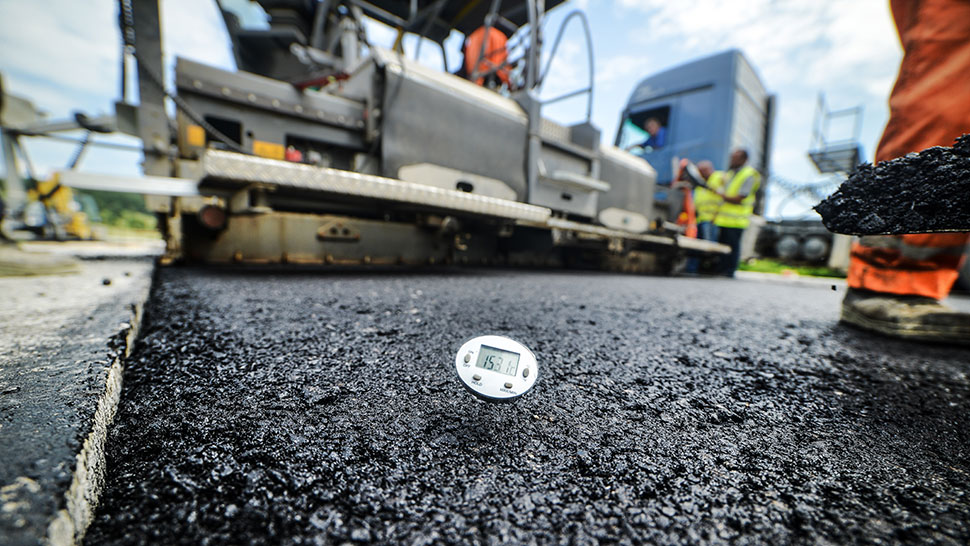
Asphalt Testing
All Construction Material Testing(CSL)
Services
Laboratory Test
Laboratory testing of soil, cement, aggregates, construction materials, and water is a critical component of civil engineering to ensure the quality, durability, and safety of infrastructure projects. Here are descriptions for each type of laboratory testing:

Cement Testing
Aggregate Testing
Water Testing

Soil Testing


Concrete Testing
Asphalt Testing
Geotechnical Testing
All Construction Material Testing
Cement Testing
Cement testing is essential to verify the quality and performance of cement used in I construction. Various tests assess parameters like fineness, setting time, compressive strength, and chemical composition. These tests ensure that the cement meets the required standards and specifications, guaranteeing the durability and strength of concrete structures.
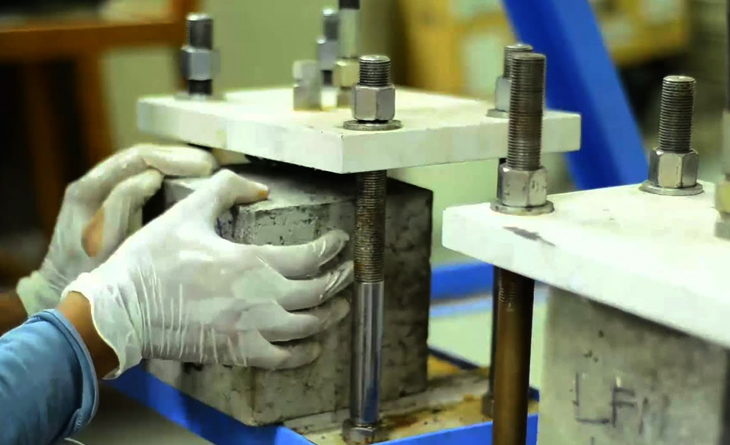
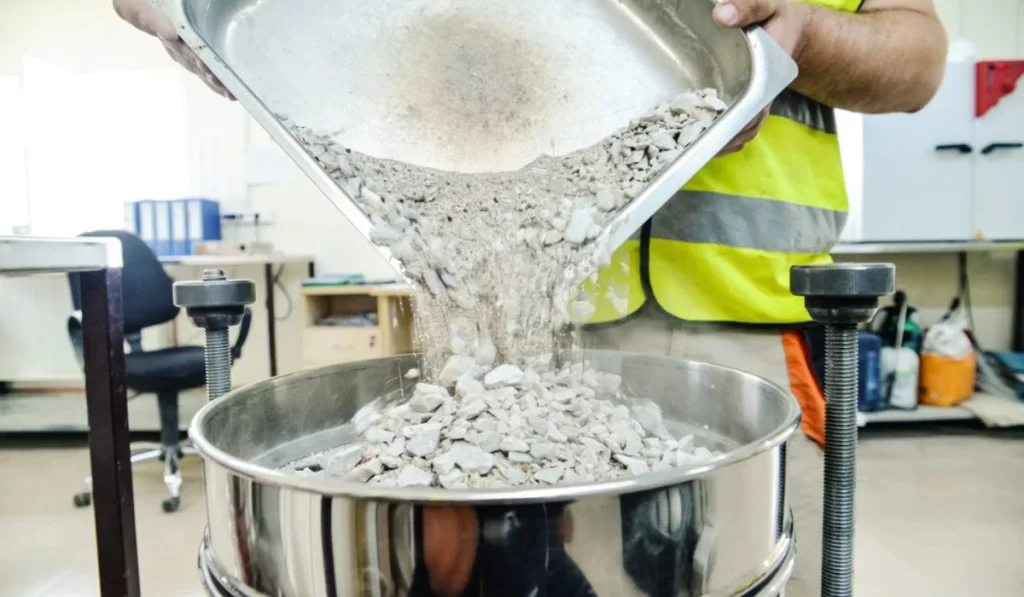


Aggregate Testing
Aggregate testing focuses on assessing the properties of aggregates (sand, gravel, crushed stone) used in concrete and asphalt. Tests include particle size distribution, moisture content, abrasion resistance, and specific gravity. Aggregate testing helps ensure the quality and consistency of materials used in construction, contributing to the strength and durability of the final product.
Water Testing
Water used in construction and infrastructure projects must meet certain qualitystandards to prevent adverse effects on materials and structures. Water testing involves assessing parameters such as pH, turbidity, chemical composition, and microbial content. This ensures that the water used in concrete mixing, curing, and other construction processes meets the required quality criteria.
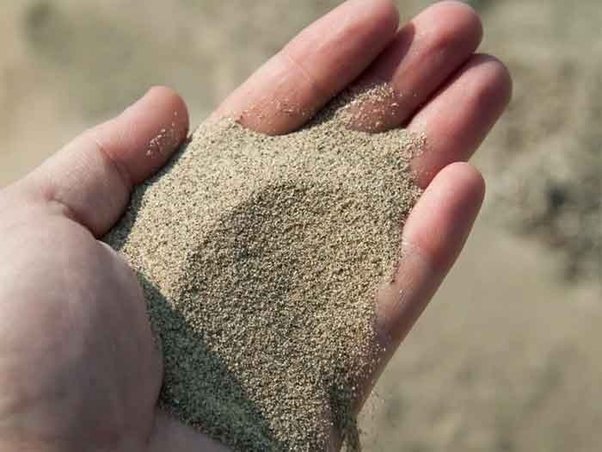


Sand Testing
Steel Testing
Steel, alloy of iron and carbon in which the carbon content ranges up to 2 percent (with a higher carbon content, the material is defined as cast iron). By far the most widely used material for building the world’s infrastructure and industries, it is used to fabricate everything from sewing needles to oil tankers.
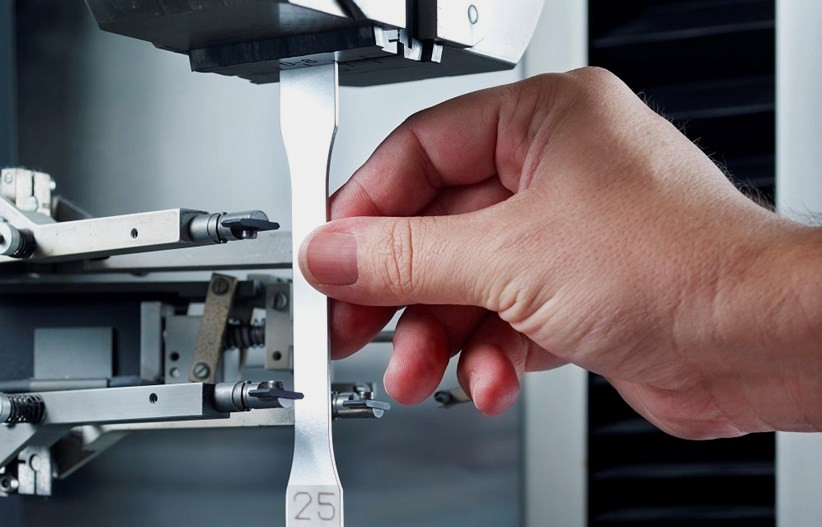
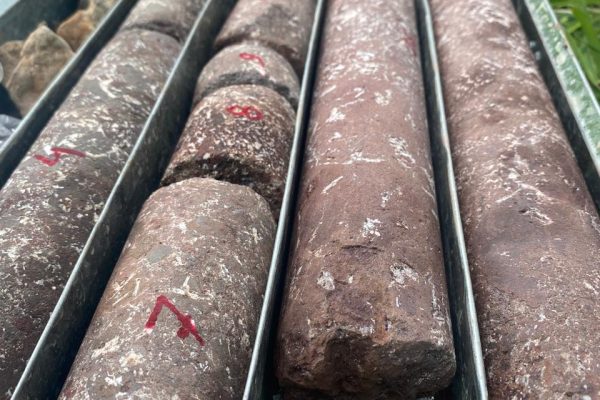


Soil Testing
Soil testing involves analyzing the physical and chemical properties of soil to assess its suitability for construction purposes. This includes tests for moisture content, density, grain size distribution, shear strength, and compaction characteristics. The data obtained from soil testing helps engineers design foundations, slopes, and other structures that can withstand the specific soil conditions at a construction site.
Bitumen Testing
To perform the float test, bitumen should first be heated to be completely liquid. Then it is poured into a mould assembly and float in a water bath at a temperature of 5 °C. Then it is submerged in a water bath at 50 °C. The time that takes the water to flow through the sample mould is recorded as float time.
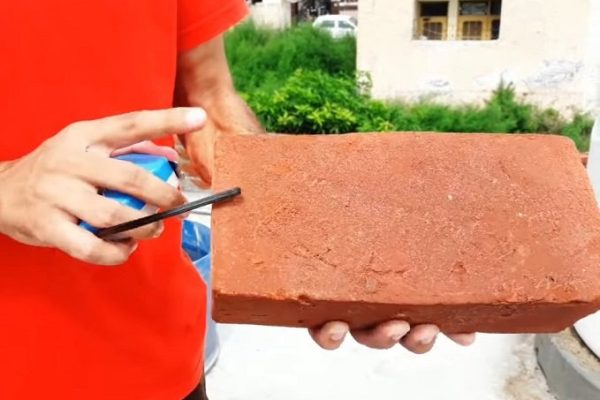


Brick Testing
Various types of tests on bricks are conducted to check the qualities of bricks for construction purposes. Tests on bricks are conducted at construction site as well as in laboratory. Bricks are oldest and important construction materials because of their durability, reliability, strength and low cost.
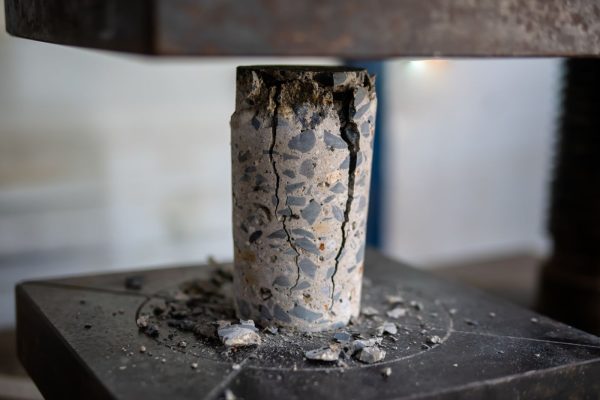

Rock Testing
Laboratory rock testing is performed to determine the strength and elastic properties of intact specimens and the potential for degradation and disintegration of the rock material. Geologists use the following tests to distinguish minerals and the rocks they make: hardness, color, streak, luster, cleavage and chemical reaction. A scratch test developed by a German mineralogist Fredriech Mohs in 1822 is used to determine mineral hardness.
Concrete Testing
Concrete testing is crucial to verify the strength, durability, and workability of concrete mixes. Tests include compressive strength testing, slump tests, and air content tests. These evaluations assist in designing concrete mixes that meet the structural requirements of a project and can endure the expected loads and environmental conditions.
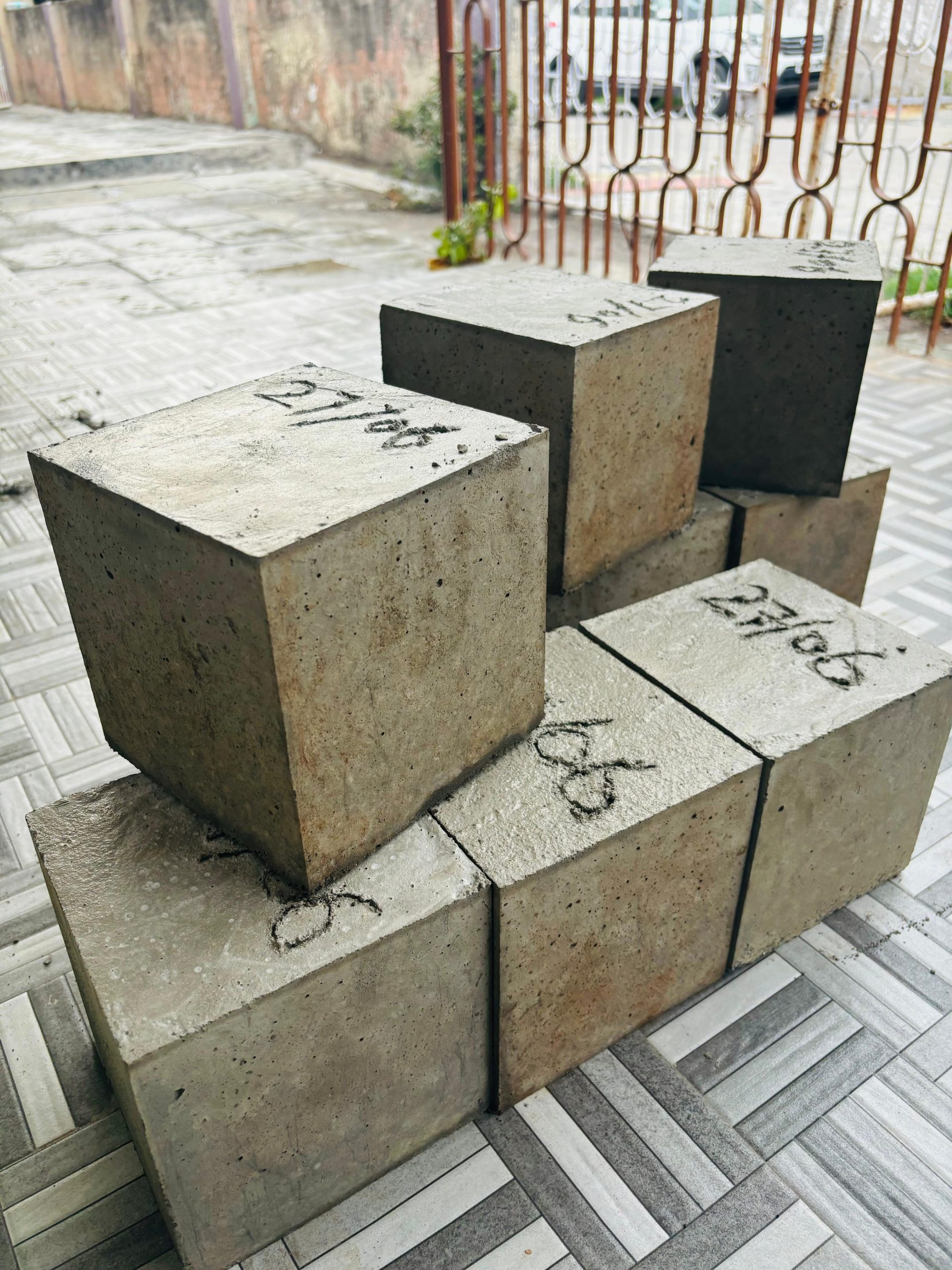
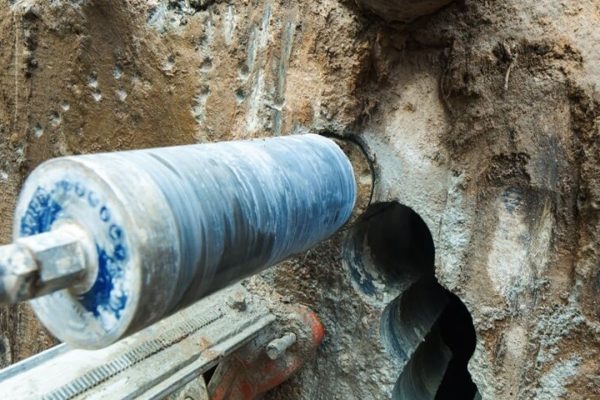


Concrete Core Testing
Construction Material Testing
This encompasses a broad range of tests conducted on various construction materials such as concrete, asphalt, bricks, and steel. These tests evaluate properties like compressive strength, tensile strength, elasticity, and durability. By ensuring that construction materials meet specified standards, engineers can confidently design structures that will perform reliably over time.

Laboratory Tests

Cement testing is essential to verify the quality and performance of cement used in I construction. Various tests assess parameters like fineness, setting time, compressive strength, and chemical composition. These tests ensure that the cement meets the required standards and specifications, guaranteeing the durability and strength of concrete structures.
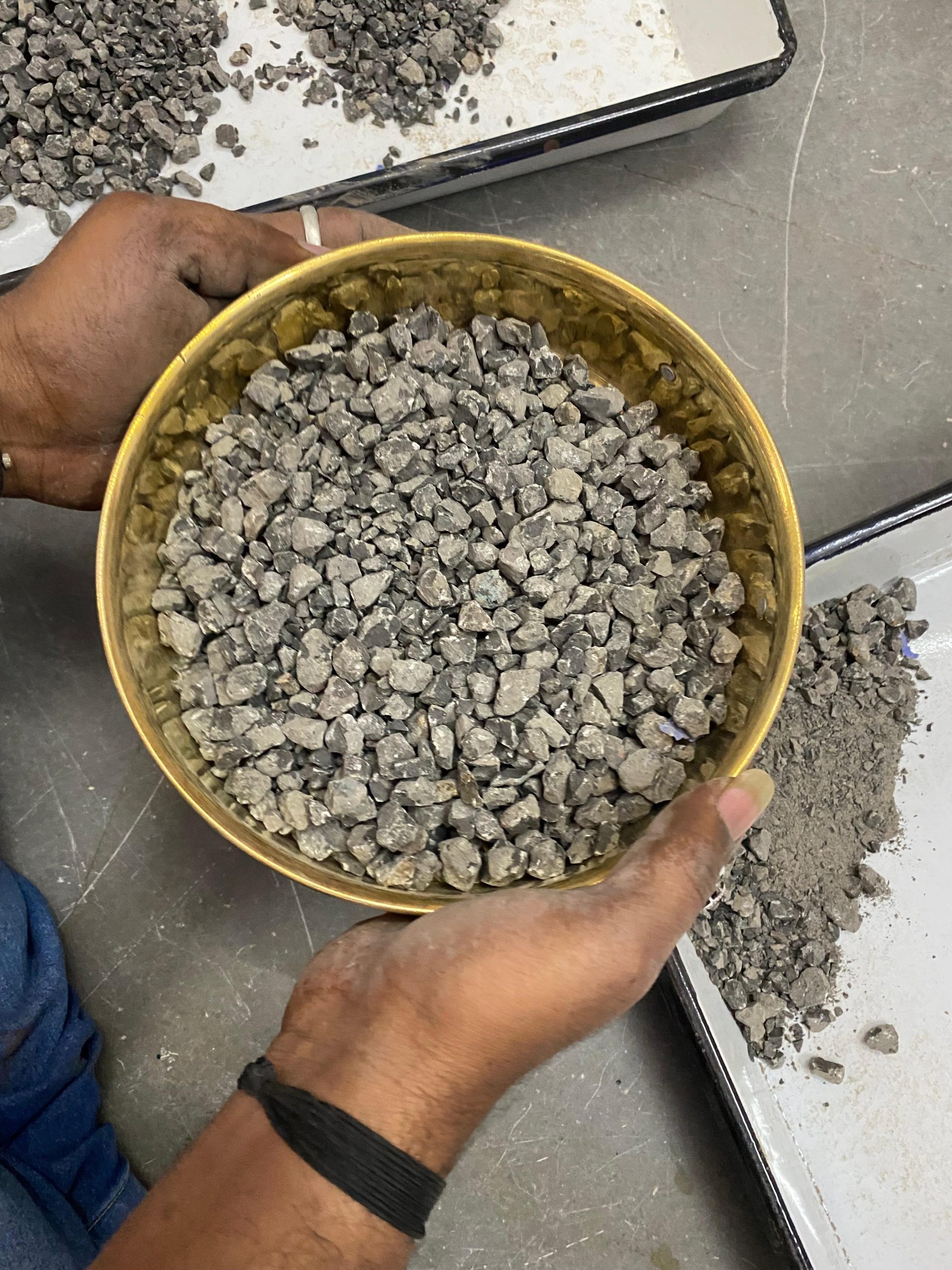

Aggregate testing focuses on assessing the properties of aggregates (sand, gravel, crushed stone) used in concrete and asphalt. Tests include particle size distribution, moisture content, abrasion resistance, and specific gravity. Aggregate testing helps ensure the quality and consistency of materials used in construction, contributing to the strength and durability of the final product.
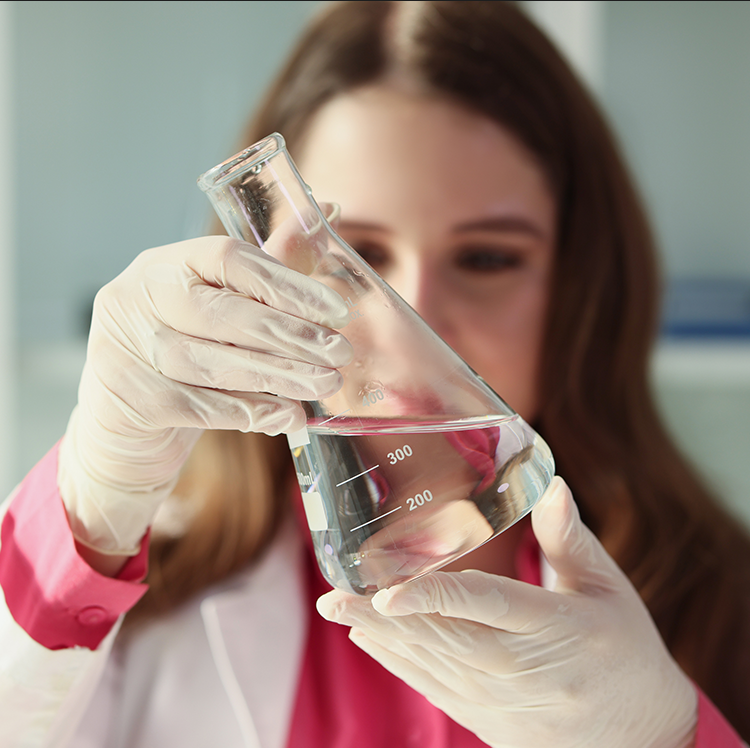

Water used in construction must meet specific quality standards to avoid compromising material strength and durability. Testing evaluates pH, turbidity, chemical composition, and microbial content to ensure suitability for concrete mixing, curing, and other processes.
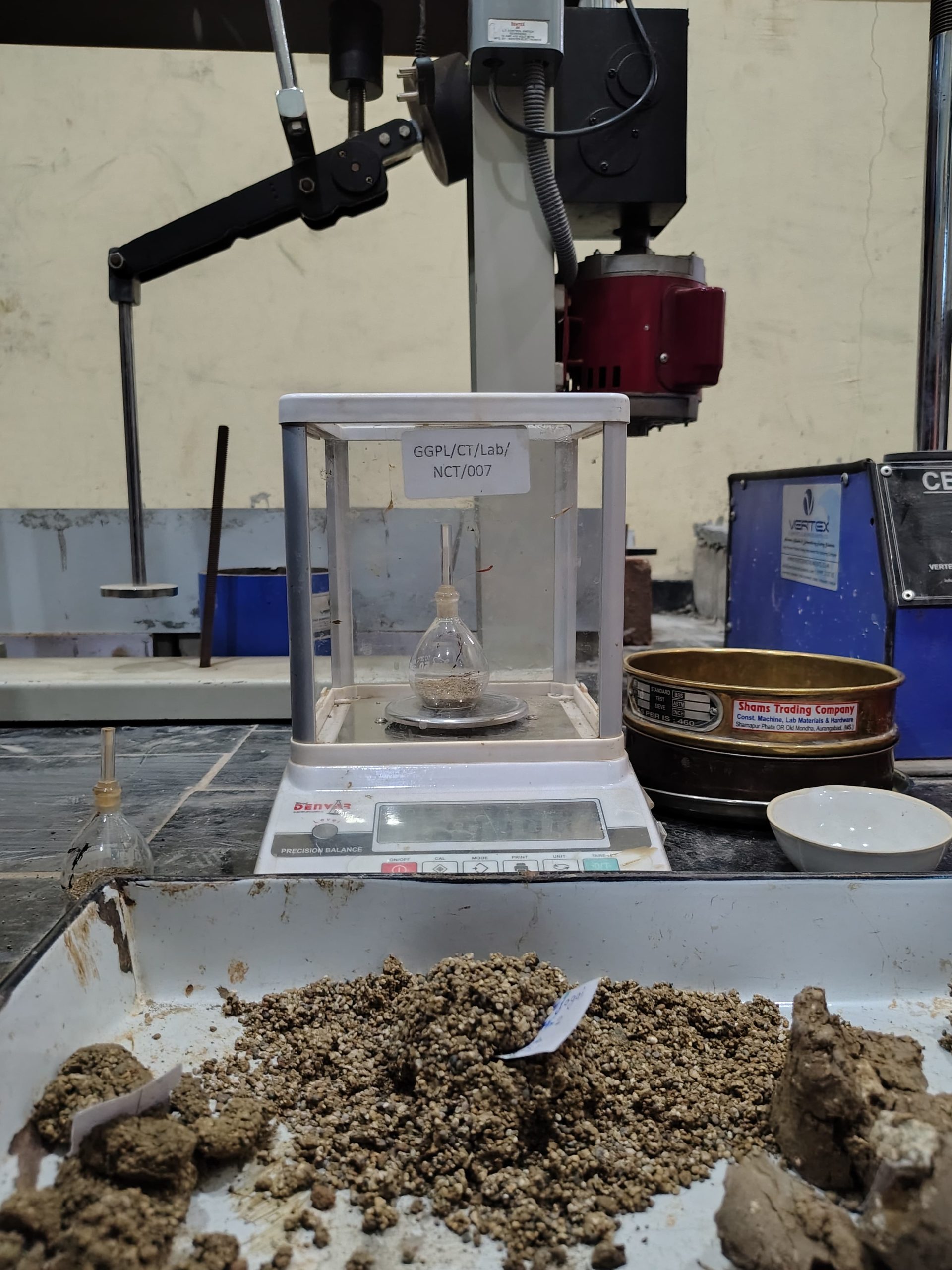

Soil testing analyzes physical and chemical properties to determine suitability for construction. It includes tests for moisture, density, grain size, shear strength, and compaction. The results guide foundation and structure design based on site conditions.

Concrete testing is crucial to verify the strength, durability, and workability of concrete mixes. Tests include compressive strength testing, slump tests, and air content tests. These evaluations assist in designing concrete mixes that meet the structural requirements of a project and can endure the expected loads and environmental conditions.
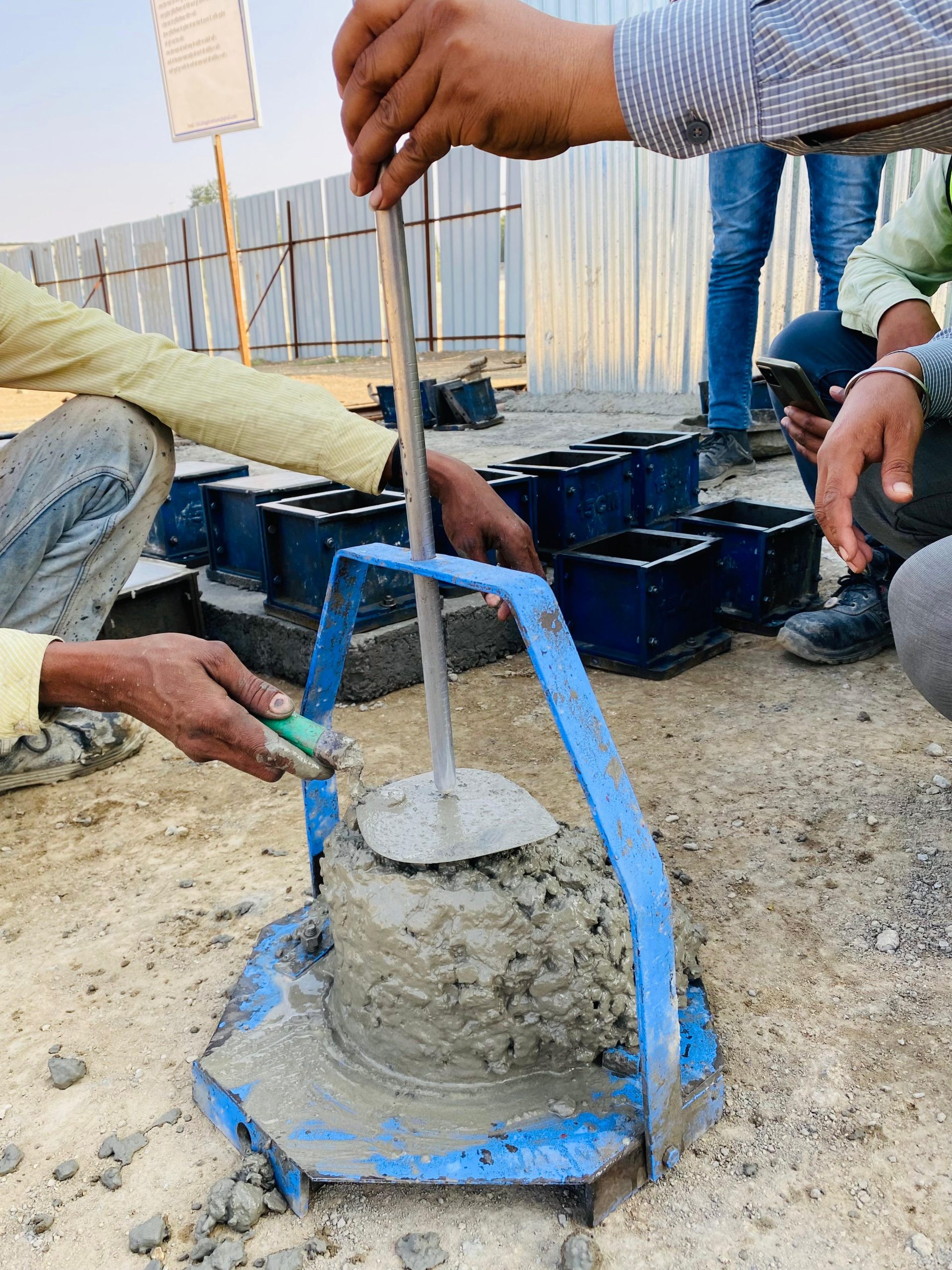

This encompasses a broad range of tests conducted on various construction materials such as concrete, asphalt, bricks, and steel. These tests evaluate properties like compressive strength, tensile strength, elasticity, and durability. By ensuring that construction materials meet specified standards, engineers can confidently design structures that will perform reliably over time.
About GeoSpectra
We specialize in providing comprehensive Geotechnical Consultancy Services .
