
Soil Test
Sieve Analysis
Sieve Analysis determines the particle size distribution of coarse-grained soils using standard sieves. It helps classify soil as gravel, sand, silt, or clay. This test is essential for foundation design, pavement construction, and compaction control to ensure soil gradation meets engineering standards.

Soil Test
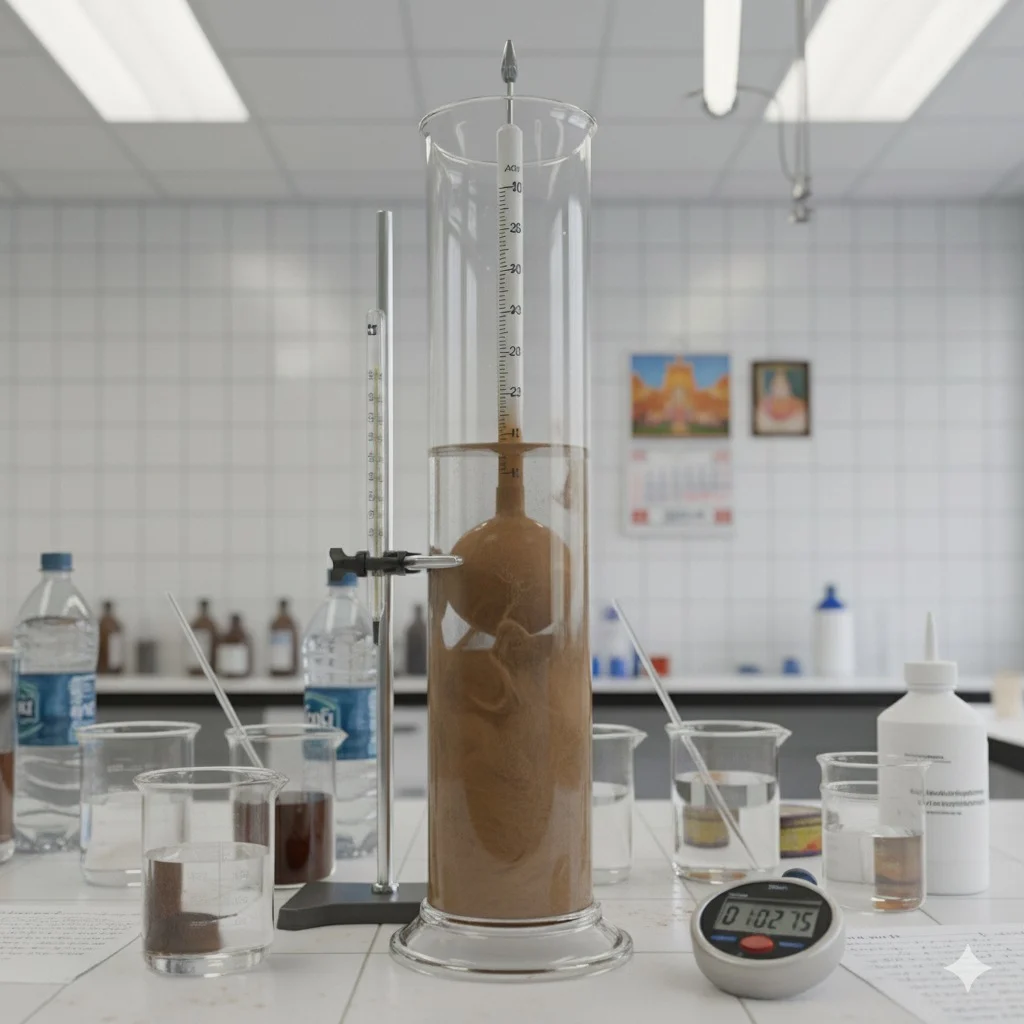
Particle Size by Hydrometer
The Hydrometer Analysis test determines the fine particle distribution of soil, including silt and clay fractions. It provides valuable data for soil classification, settlement prediction, and permeability analysis, making it essential for geotechnical design and foundation engineering.

Soil Test
Specific Gravity
This test measures the ratio of soil solids to the weight of an equal volume of water. It helps calculate important soil parameters like void ratio, porosity, and degree of saturation. Specific gravity values assist in identifying soil composition and strength behavior.

Soil Test
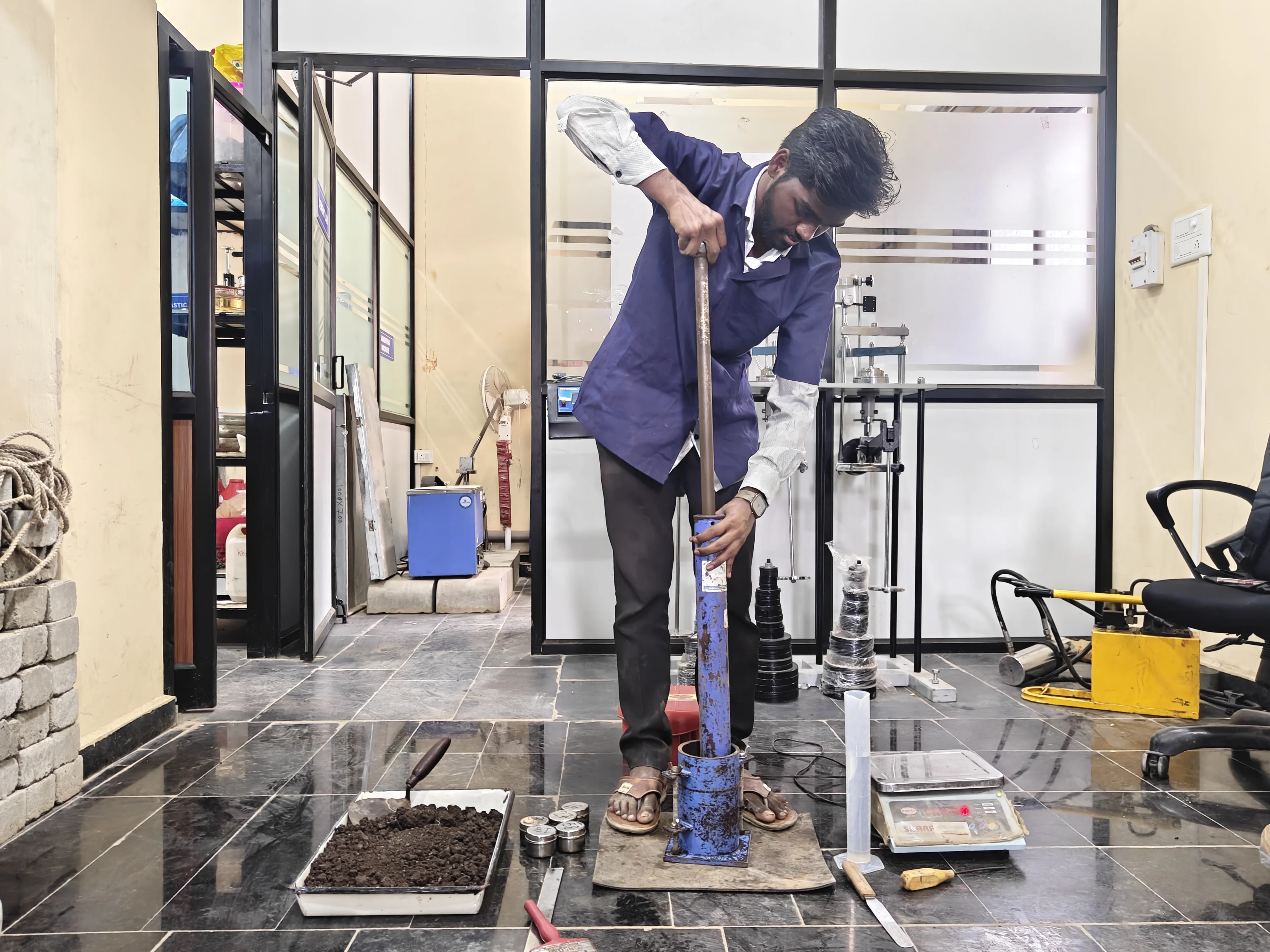
Natural Moisture Content
Determines the natural water content in soil, indicating its strength, compressibility, and workability. Moisture content is crucial for assessing soil suitability in construction and compaction projects.

Soil Test
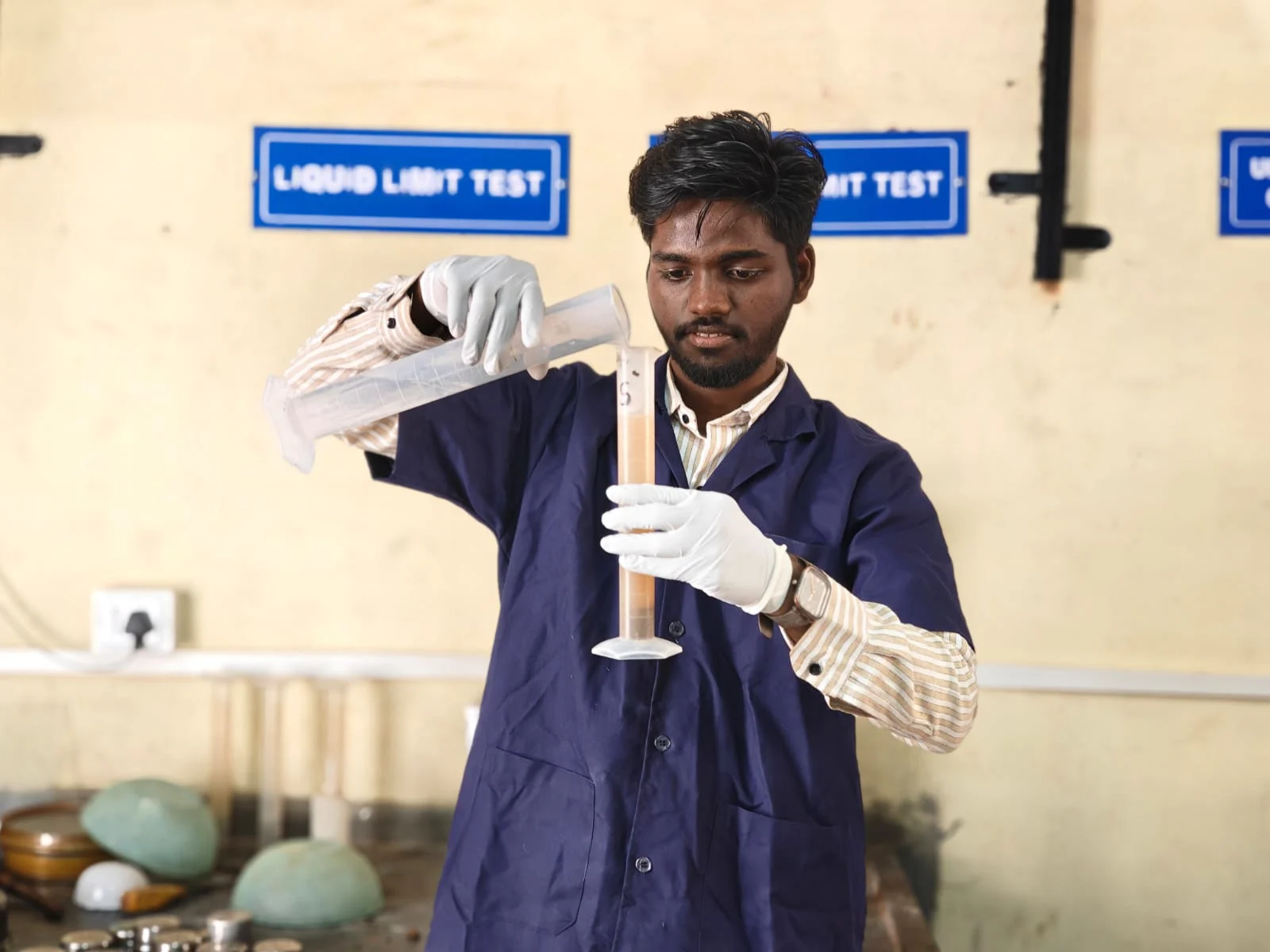
Liquid Limit
Determines the moisture content at which soil changes from plastic to liquid state. It indicates soil plasticity and helps classify soils under Atterberg Limits, useful for predicting behavior in wet conditions.

Soil Test
Plastic Limit
Identifies the lowest moisture content at which soil can be molded without cracking. It defines the plasticity index and helps evaluate soil consistency and workability.

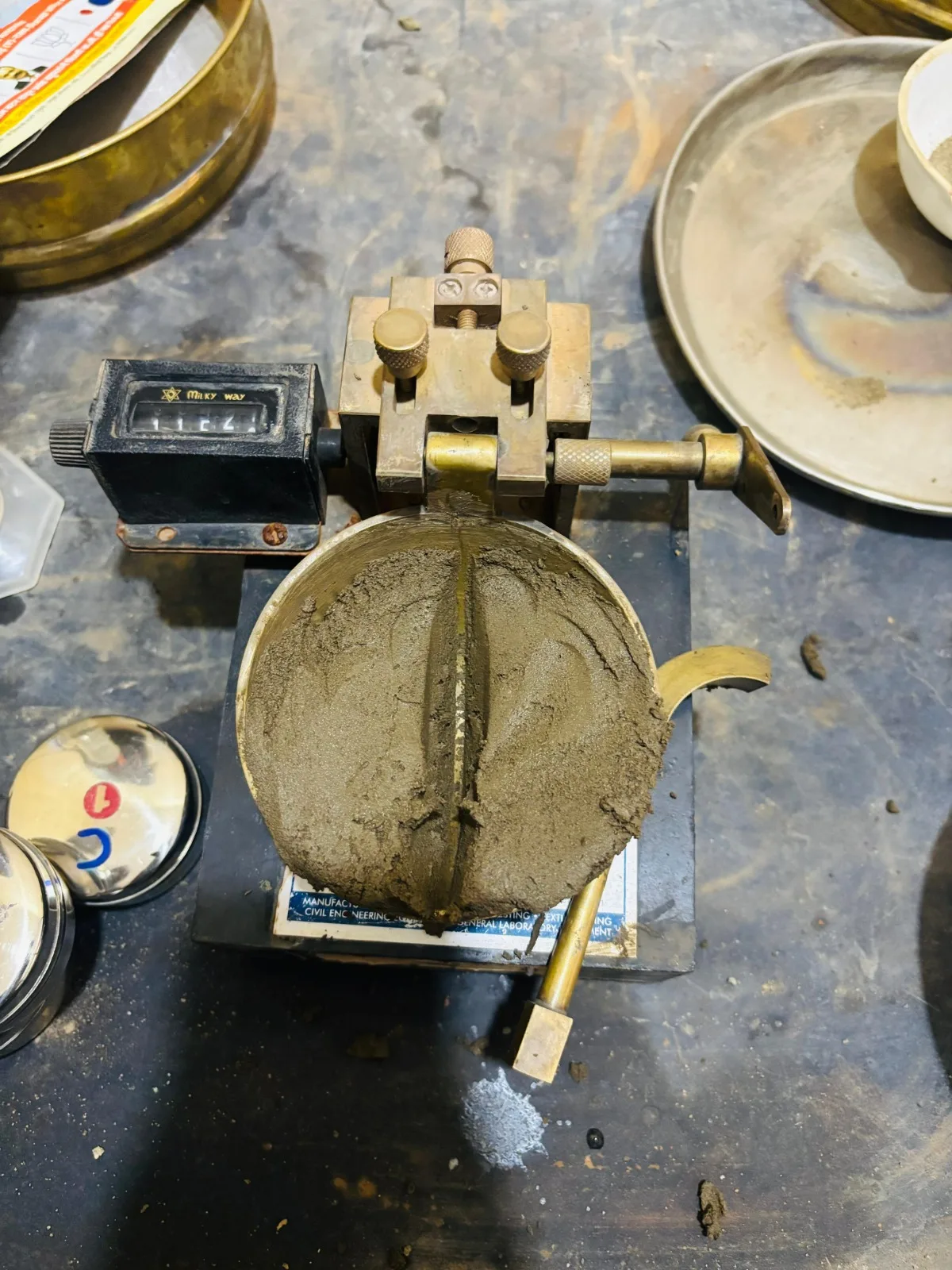
Soil Test
Shrinkage Limit
Determines the lowest moisture content where further drying causes no volume change. It helps assess soil shrinkage or swelling potential, vital for expansive clay foundations.

Soil Test
Free Swell Index
Measures the increase in soil volume when soaked in water. It helps identify expansive soils that can cause foundation heaving or cracking.

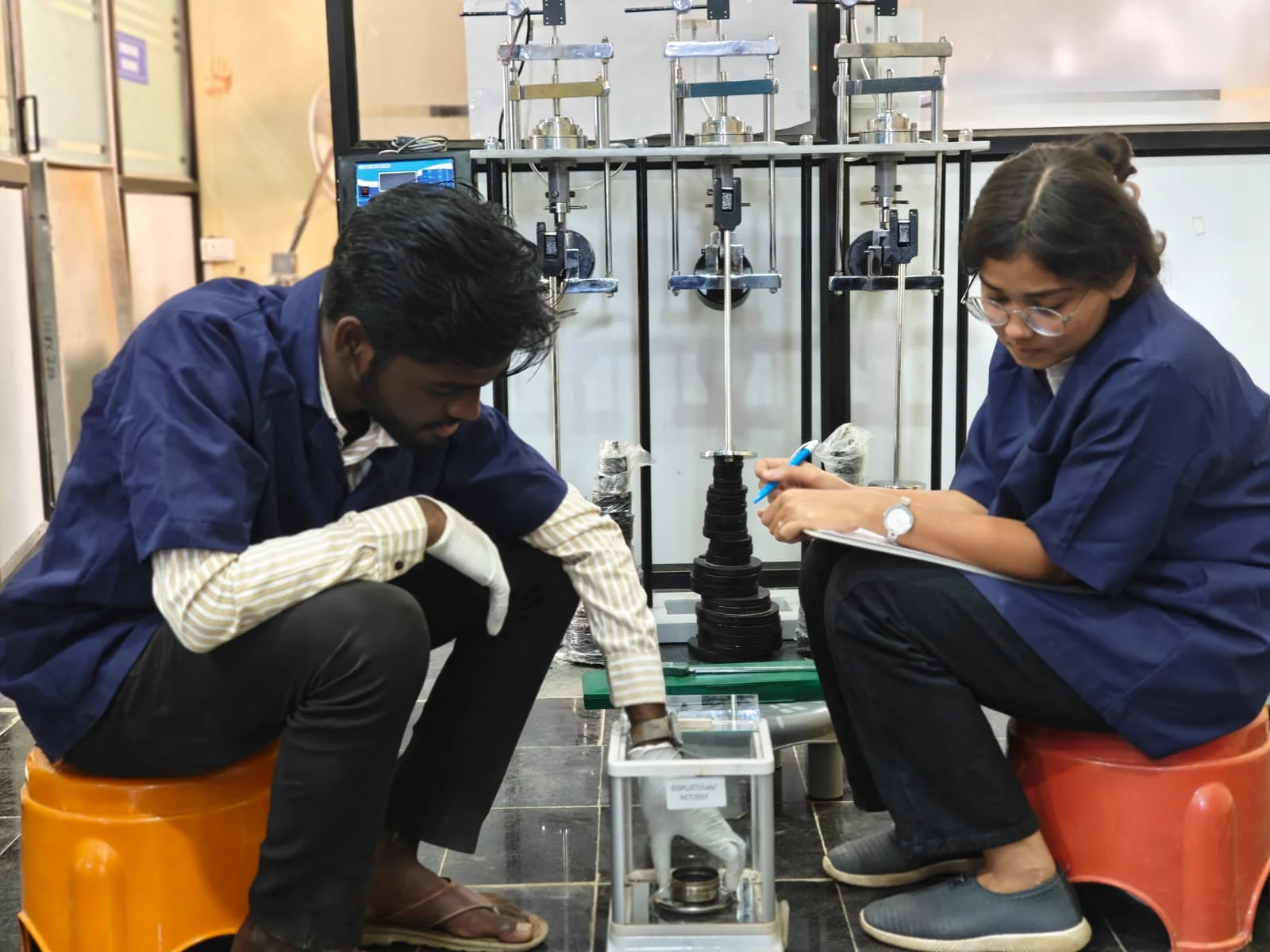
Soil Test
Heavy and light compaction test
Determines the relationship between moisture content and dry density. Helps find the optimum moisture for maximum soil compaction in road and earthwork projects.
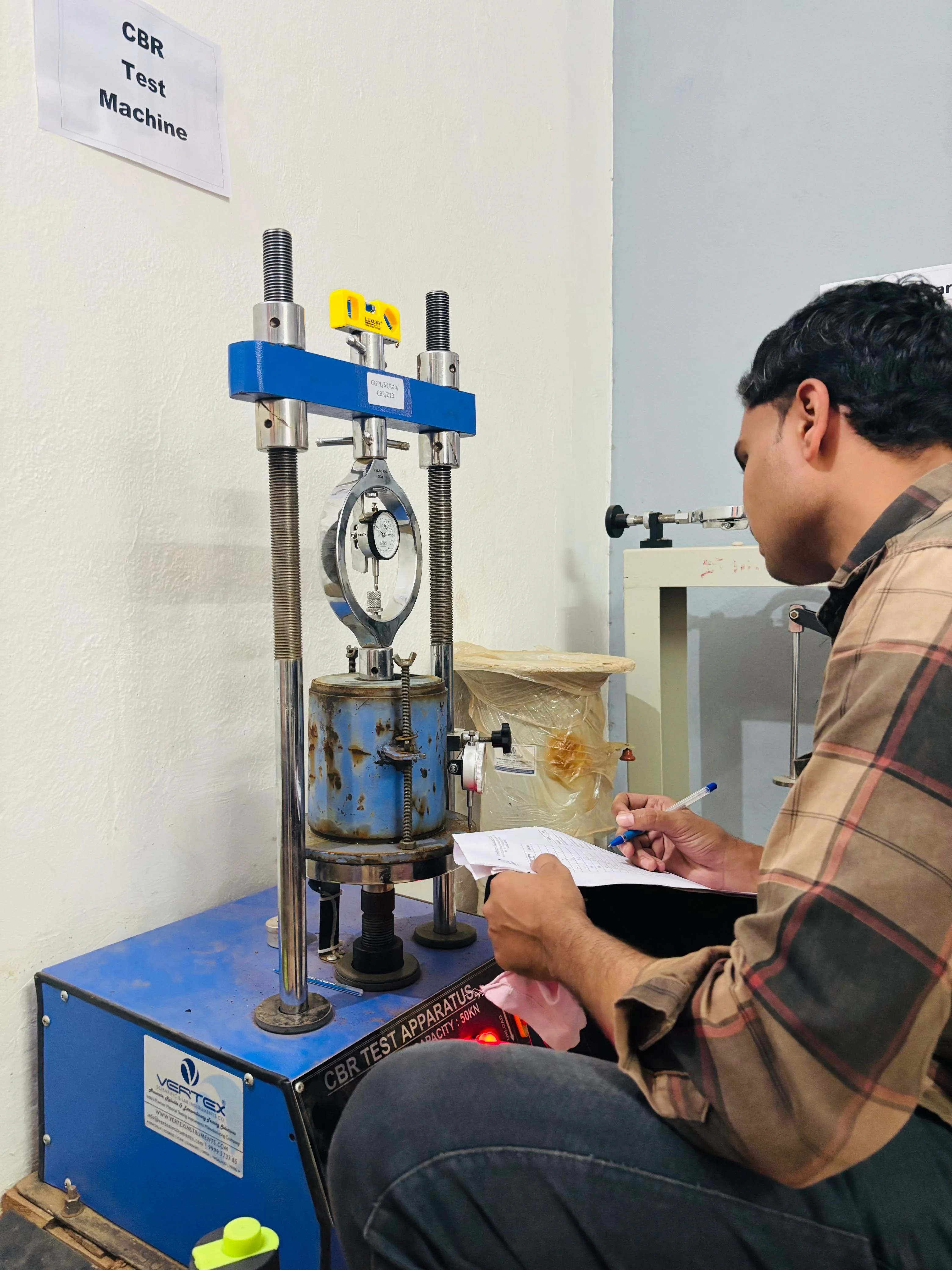

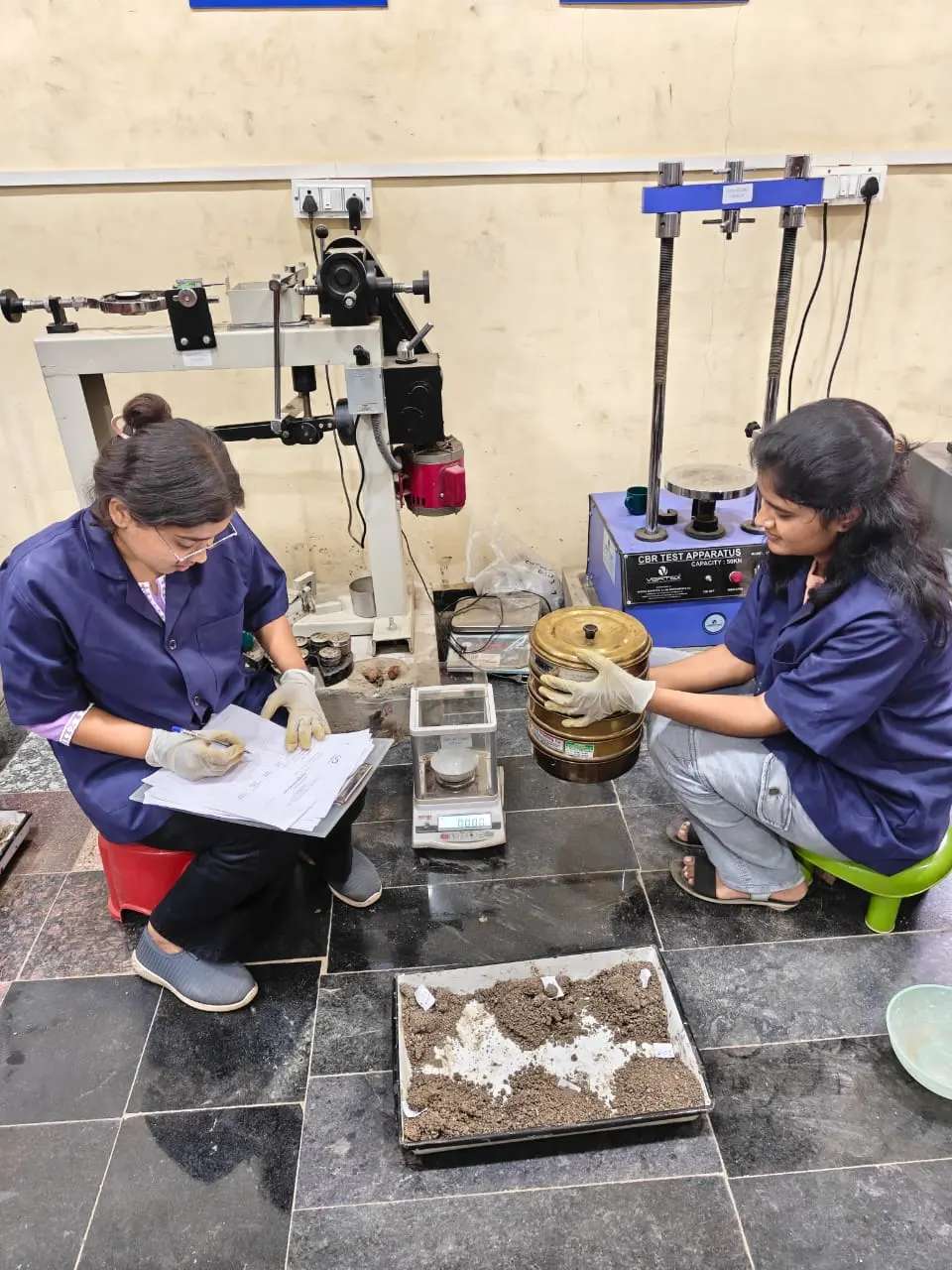
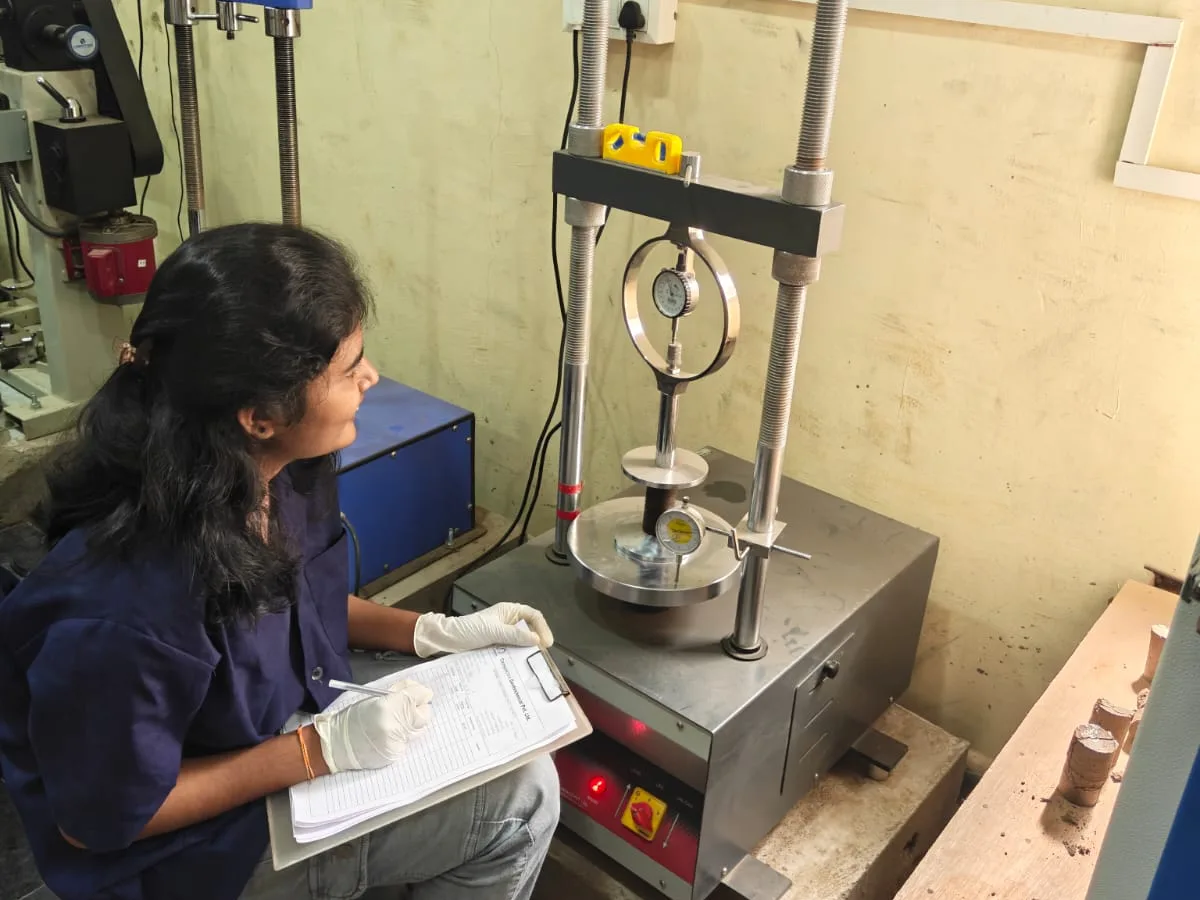
Soil Test
California Bearing Ratio (CBR)
Assesses the load-bearing capacity of soil for pavements. Higher CBR values mean stronger subgrades suitable for roads and highways.

Soil Test
Unconfined Compressive Strength
Evaluates the compressive strength of cohesive soils without confinement. Used for foundation design and slope stability assessment.
Soil Test
Triaxial Compression Test (UU, CU, CD)
The Triaxial Compression test determines the shear strength of soil under controlled drainage and confining pressure conditions. It provides accurate data for slope stability, foundation design, and earth pressure analysis.
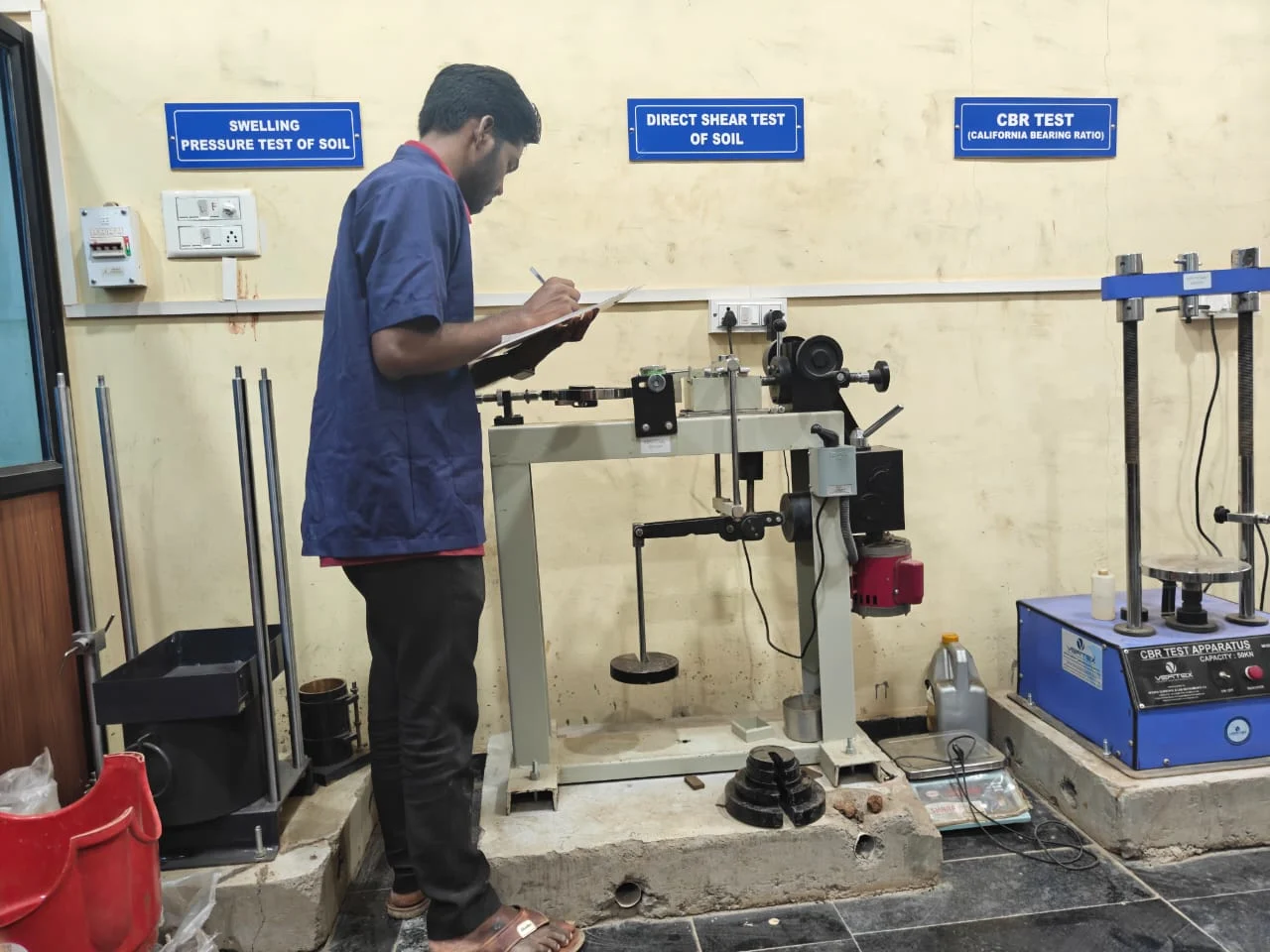

Soil Test
Direct Shear Test (UU, CU, CD)
Measures soil shear strength by applying a horizontal force on a prepared sample. It helps calculate cohesion and the angle of internal friction. This test is widely used for designing slopes, retaining walls, and shallow foundations.
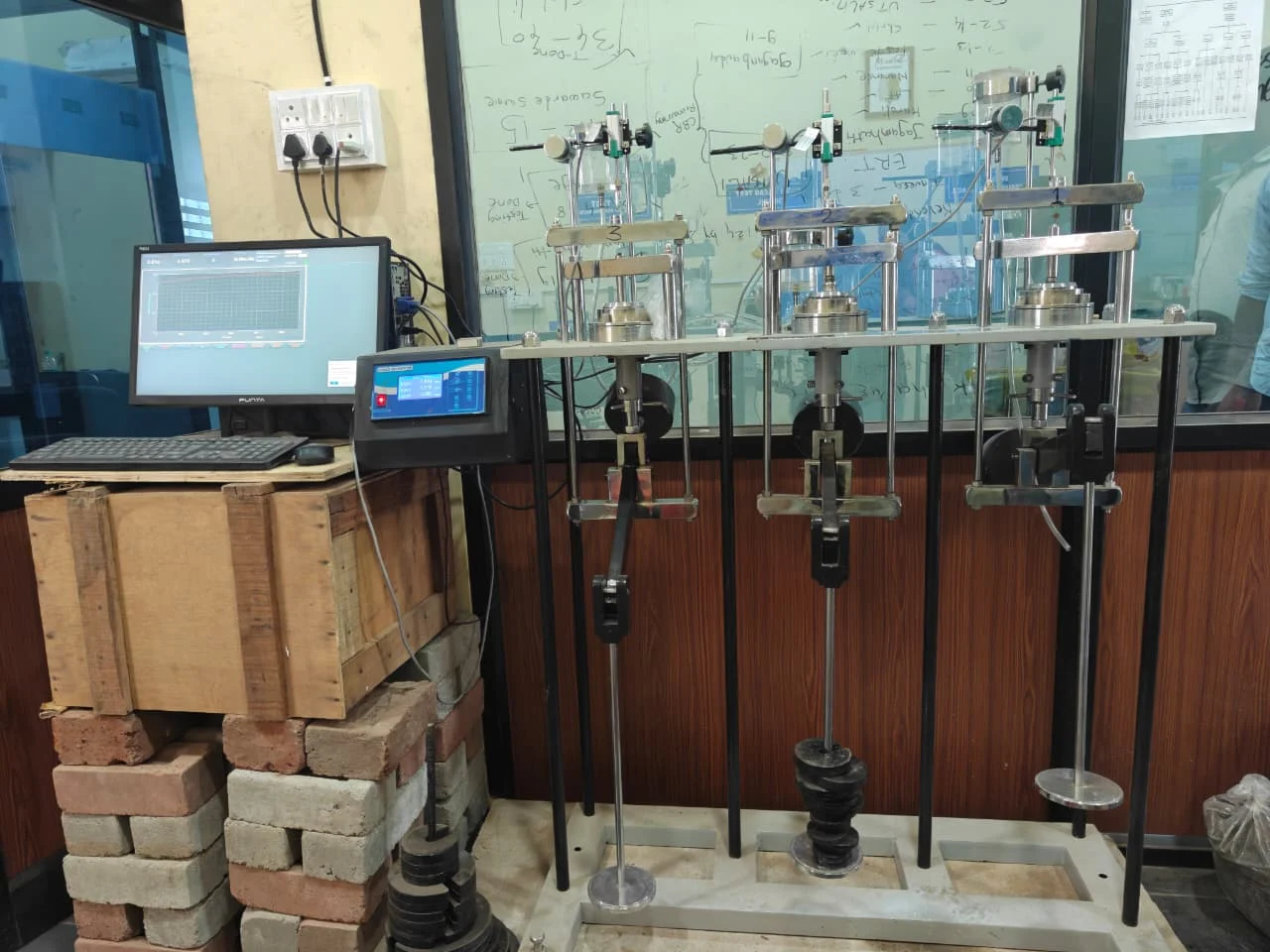

Soil Test
Consolidation Test
This test measures soil settlement over time under applied loads. It is critical for predicting foundation settlement and designing safe structures.
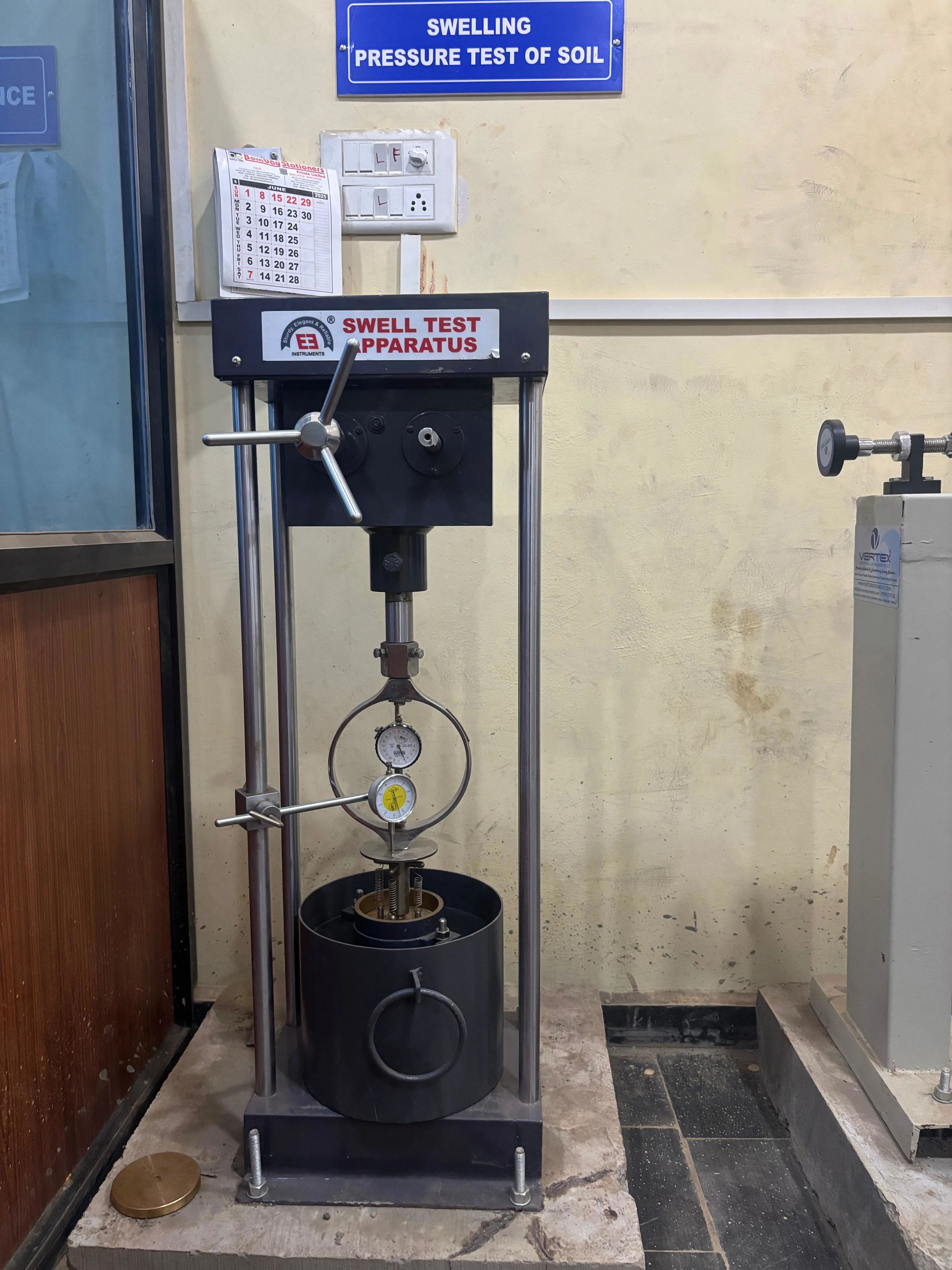

Soil Test
Swelling Pressure Test
Determines the pressure exerted by expansive soil when it swells upon wetting. It helps assess the swelling potential of clayey soils. The results guide engineers in foundation design and soil stabilization measures.

Soil Test
Lab Vane Shear Test
The Lab Vane Shear test quickly measures the undrained shear strength of cohesive soils using a rotating vane. It’s ideal for soft clays and helps evaluate short-term soil stability under construction loads.

Soil Test
Silt Factor
The Silt Factor test assesses the fineness of soil particles, which affects erosion and sedimentation characteristics. It’s particularly useful in designing canals, riverbeds, and other hydraulic structures.

Soil Test
Permeability by Constant Head
This test measures how easily water flows through coarse-grained soils under a steady hydraulic head. It’s essential for drainage design, seepage studies, and groundwater movement analysis.

Soil Test
Permeability by Falling Head
Used to determine the permeability of fine-grained soils where water flows slowly. It provides valuable data for seepage and soil drainage design in silty and clayey soils.

Soil Test
Soil & Sand Equivalent Test
The Sand Equivalent test compares the cleanliness of sand to the amount of clay-like material in soil. It ensures the quality of materials used in road construction and base layers.

Rock Tests
Compressive Strength of Natural Rock
Determines the maximum load a rock can bear before failure. It helps evaluate stone durability for construction and foundation design.
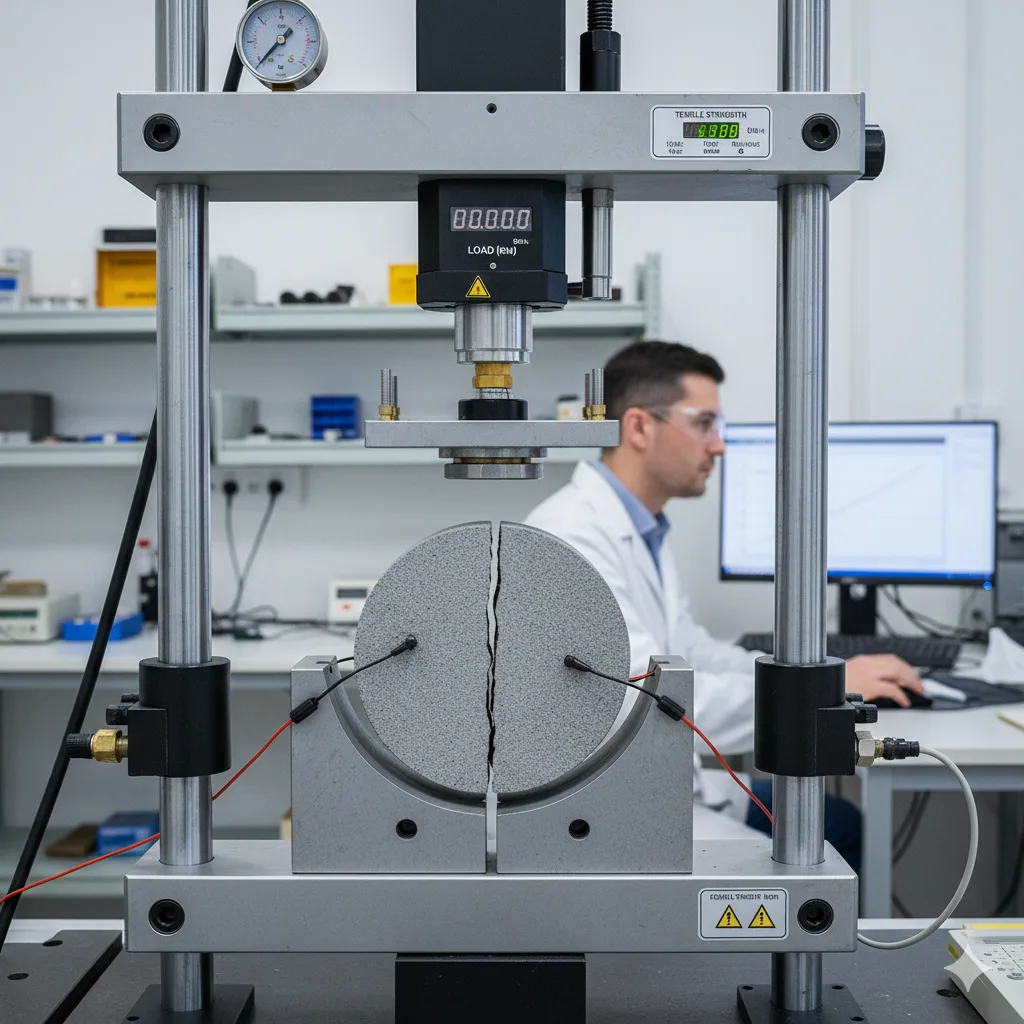

Rock Tests
Tensile Strength of Natural Rock
The Tensile Strength Test measures a stone’s resistance to cracking under tension. It is essential for evaluating durability, structural performance, and suitability of natural stones in construction projects.

Rock Tests
Porosity
The Porosity Test measures the void spaces within rocks, influencing permeability, durability, and compressive strength. It is essential for evaluating natural stone quality and suitability in construction projects.

Rock Tests
Specific Gravity
The Specific Gravity Test measures the density of rocks relative to water. It is essential for assessing porosity, strength, and design parameters, ensuring the quality and suitability of natural stones in construction projects.

Rock Tests
Water Absorption
The Water Absorption Test measures the amount of water a stone can absorb. High absorption affects durability, weathering resistance, and overall performance of natural stones in construction projects.

Rock Tests
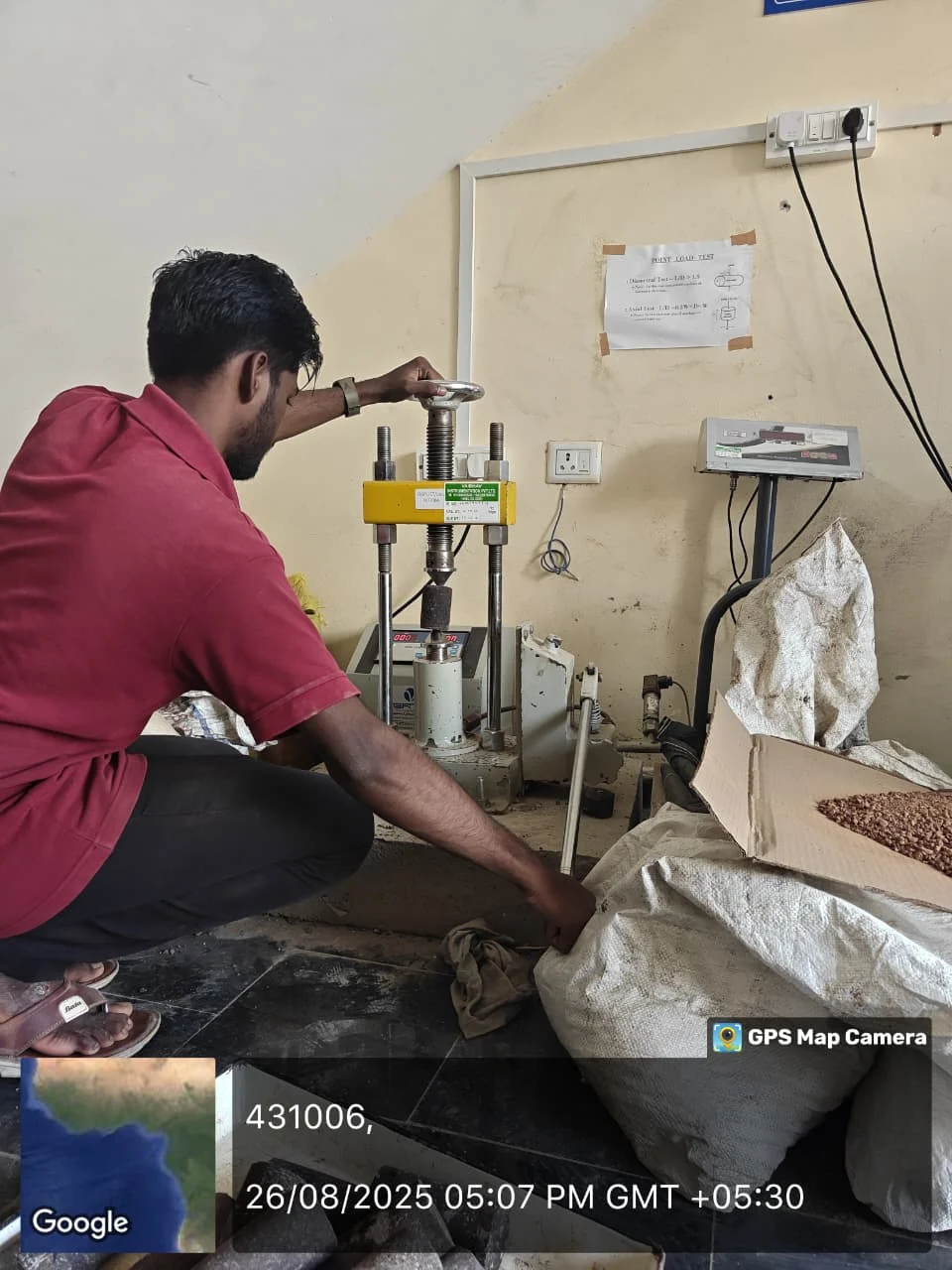
Point Load Index
The Point Load Test measures the strength of rock under a concentrated load. It provides a quick and reliable method for evaluating rock quality and durability in field and construction applications.

Rock Tests
Rock Triaxial Test
The Triaxial Test evaluates the shear and compressive strength of rocks under controlled axial and lateral stresses. It is essential for predicting rock behavior, stability, and performance under field loading conditions in construction and engineering projects.

Rock Tests
Brazilian Tensile Strength of Rock
The Brazilian Test measures the tensile strength of rocks using diametral compression on a cylindrical sample. It is essential for evaluating rock durability, slope stability, and the design of rock structures in construction and engineering projects.

Rock Tests
Transverse Strength of Natural Stones
The Transverse Strength Test measures the bending strength of stone beams. It is essential for designing durable pavements, slabs, and other structural elements in construction projects.

Cement Tests
Compressive Strength
The Compressive Strength Test measures the ability of cement to withstand axial loads. It is essential for evaluating cement quality, performance, and reliability in concrete structures and construction projects.

Cement Tests
Normal Consistency
The Normal Consistency Test measures the water required to prepare a cement paste of standard consistency. It is essential for proper mixing, hydration, and performance of cement in concrete construction.

Cement Tests
Density
The Density Test measures the mass per unit volume of cement. Accurate density values are essential for concrete mix design, quality control, and ensuring optimal performance in construction projects.

Cement Tests
Final Setting Time
The Final Setting Time Test measures how long it takes for cement paste to harden completely. It ensures adequate working time and proper setting for concrete and construction activities.
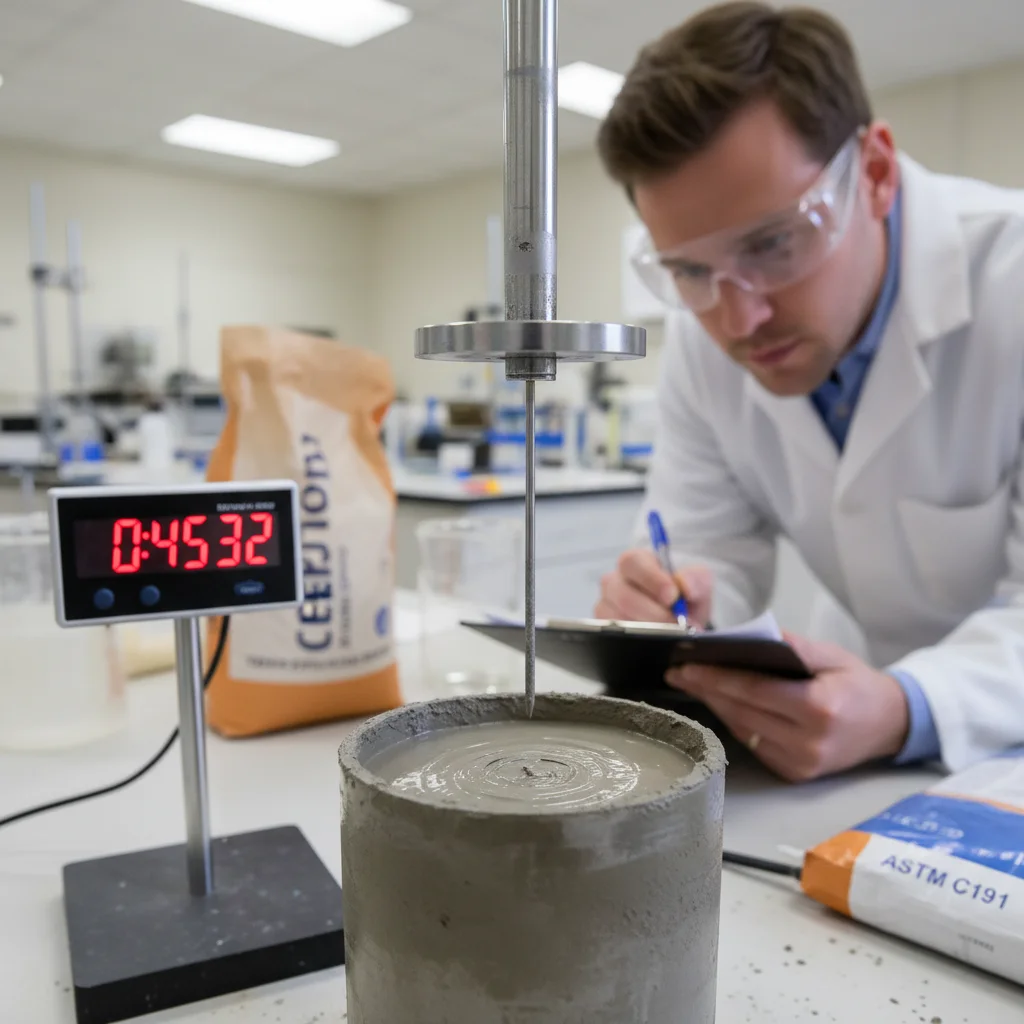

Cement Tests
Initial Setting Time
The Initial Setting Time Test measures the time required for cement paste to begin stiffening. It is essential for planning mixing, transporting, and placing concrete in construction projects.
Cement Tests
Soundness By Le-Chatelier
The Soundness Test evaluates cement for excessive expansion caused by unhydrated lime. It ensures durability, prevents cracking, and guarantees long-term performance of concrete structures.

Cement Tests
Fineness by Dry Sieving
The Fineness Test measures the particle size distribution of cement. Proper fineness ensures efficient hydration, improved strength development, and optimal workability of concrete in construction projects.

Fine Aggregates Tests
Bulk Density
The Bulk Density Test measures the mass of fine aggregates per unit volume. It is essential for evaluating compaction characteristics and designing accurate concrete mix proportions in construction projects.

Fine Aggregates Tests
Material Finer Than 75 Micron
The Material Finer Than 75 Micron Test measures the proportion of fine particles in aggregates. Excess fines can negatively impact concrete workability, strength, and durability in construction projects.
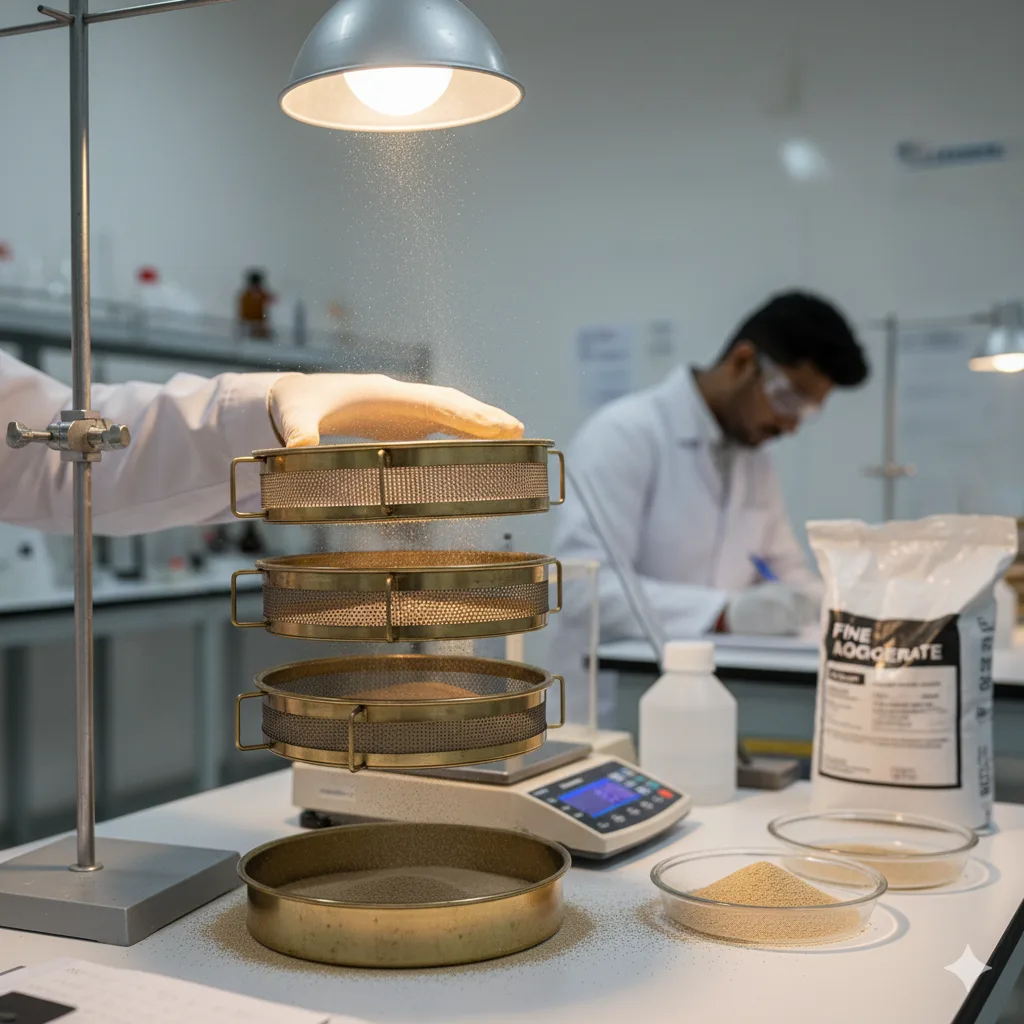

Fine Aggregates Tests
Sieve Analysis
The Sieve Analysis Test determines the particle size distribution of fine aggregates. It is essential for proper grading, improving concrete workability, and ensuring strength and durability in construction projects.
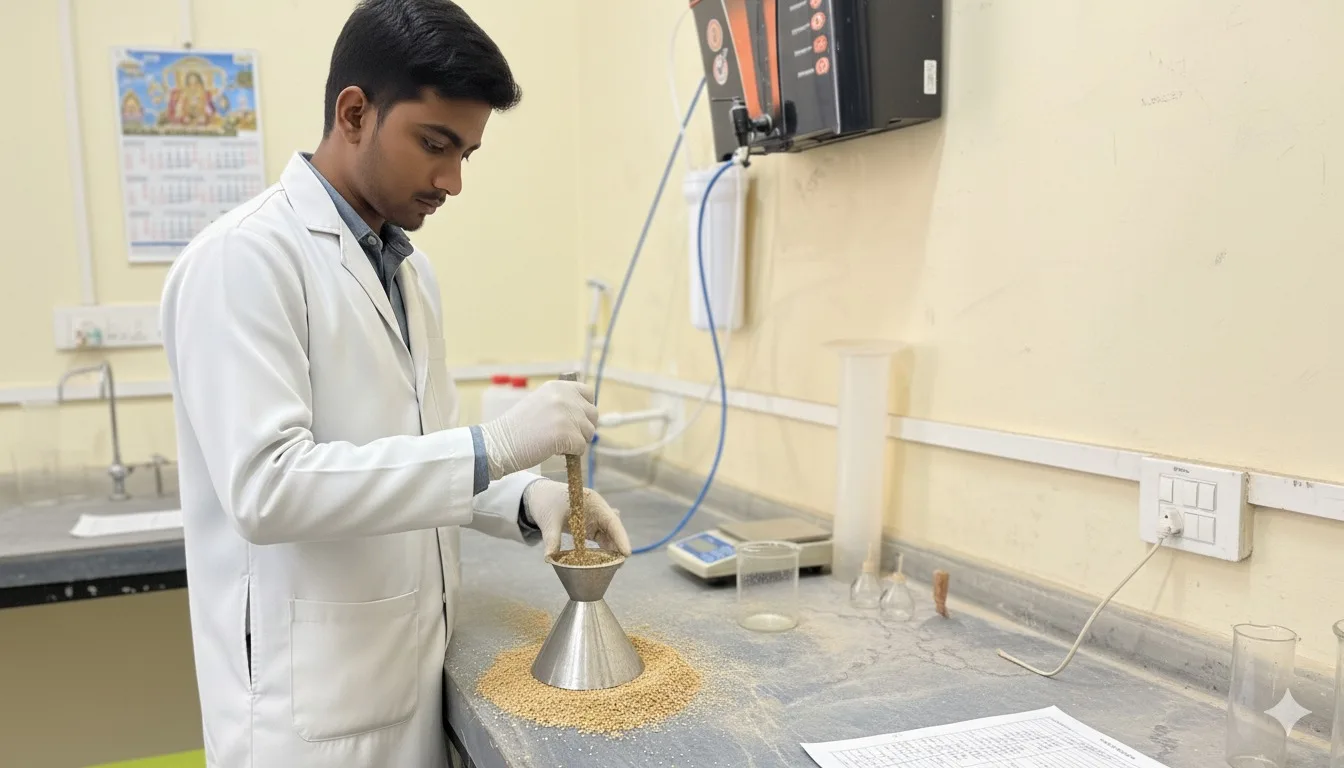

Fine Aggregates Tests
Water Absorption
The Water Absorption Test measures the ability of aggregates to absorb water. It is essential for adjusting water content in concrete mix design, ensuring optimal workability, strength, and durability in construction projects.
Fine Aggregates Tests
Specific Gravity
The Specific Gravity Test measures the density of aggregates relative to water. It is crucial for accurate concrete mix design, quality control, and ensuring the strength and durability of construction projects.

Fine Aggregates Tests
Sulphate Soundness (Magnesium & Sodium)
The Sulphate Soundness Test evaluates the durability of fine aggregates against chemical attack by sulphates. It helps prevent expansion, deterioration, and ensures long-term strength and stability of concrete structures.

Coarse Aggregates Tests
Flakiness Index
The Flakiness Index Test measures the percentage of flaky particles in coarse aggregates. It is essential for assessing workability, compaction, and ensuring the strength and durability of concrete in construction projects.

Coarse Aggregates Tests
Elongation Index
The Elongation Index Test measures the proportion of elongated particles in aggregates. Excess elongated particles can reduce concrete strength and durability by causing uneven stress distribution in construction projects.

Coarse Aggregates Tests
10% Fine Value
The 10% Fine Value Test measures the strength of coarse aggregates containing up to 10% fines. It is essential for assessing aggregate durability, crushing resistance, and suitability for concrete and road construction projects.
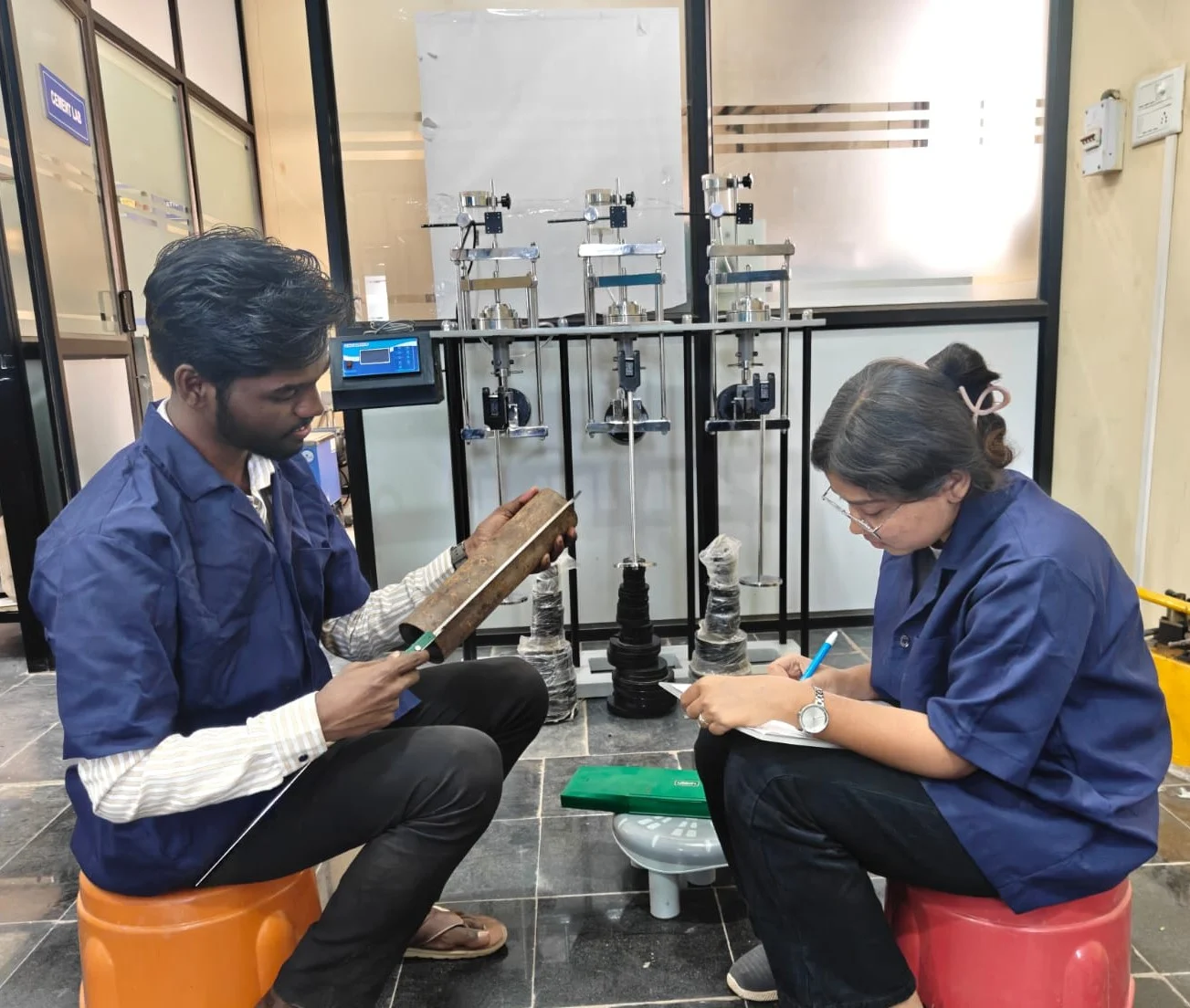

Coarse Aggregates Tests
Bulk Density
The Bulk Density Test measures the mass per unit volume of coarse aggregates. It is essential for accurate concrete mix design, compaction analysis, and ensuring strength and durability in construction projects.
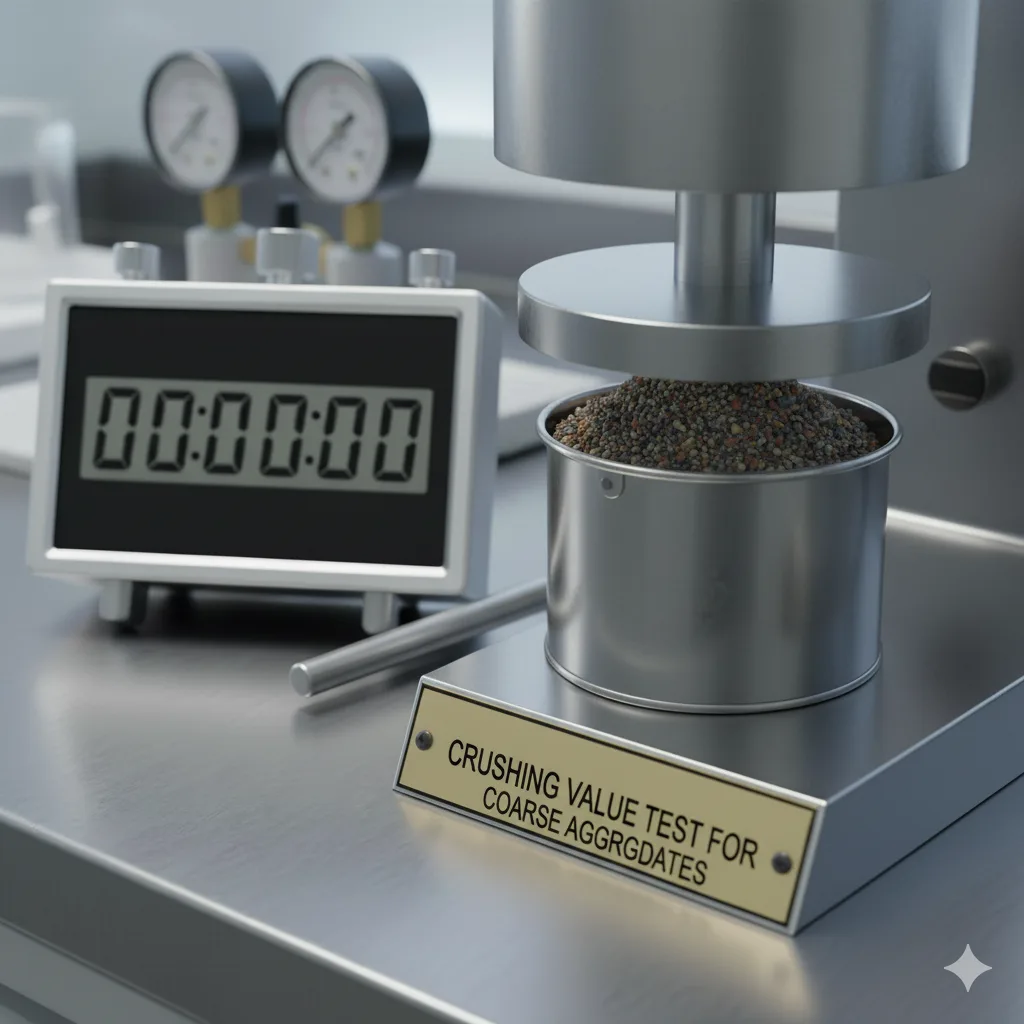

Coarse Aggregates Tests
Crushing Value Test
The Crushing Value Test measures the resistance of aggregates to crushing under compressive load. It ensures aggregates are durable and suitable for structural concrete and construction projects.

Coarse Aggregates Tests
Impact Test
The Impact Test evaluates the toughness of coarse aggregates under sudden loads. High resistance ensures durability, strength, and long-term performance of pavements and concrete structures in construction projects.
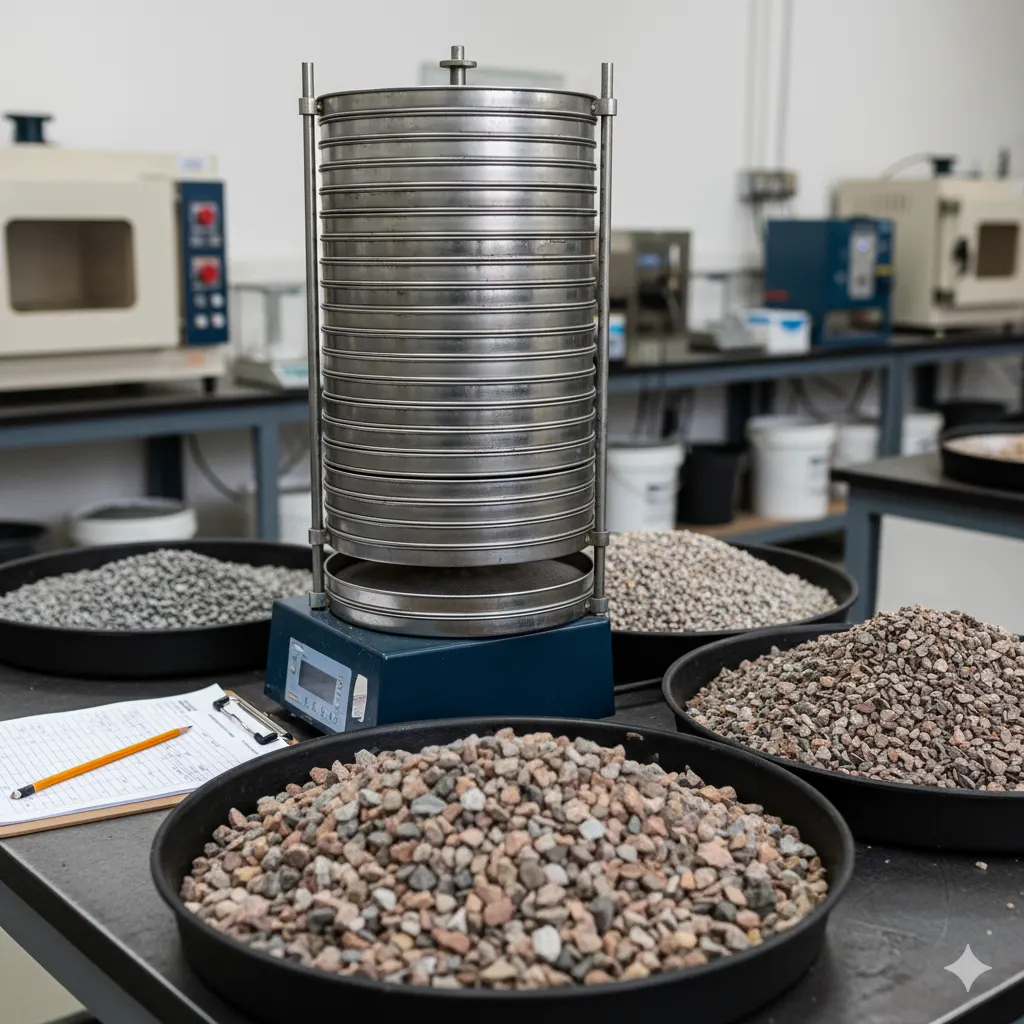

Coarse Aggregates Tests
Sieve Analysis
The Sieve Analysis Test determines the particle size distribution of coarse aggregates. Proper grading ensures optimal workability, strength, and durability of concrete in construction projects.
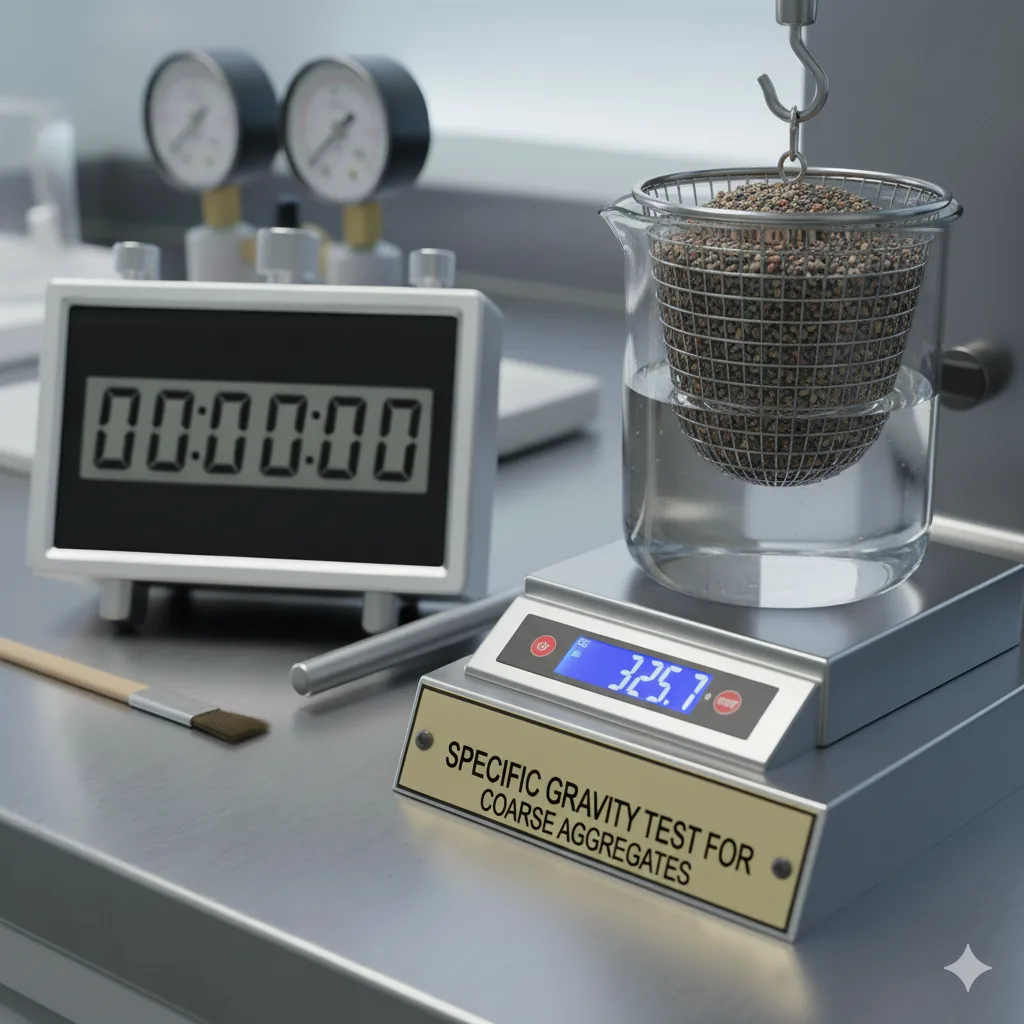

Coarse Aggregates Tests
Specific Gravity
The Specific Gravity Test measures the density of coarse aggregates relative to water. It is essential for accurate concrete mix design, quality control, and ensuring strength and durability in construction projects.

Coarse Aggregates Tests
Water Absorption
The Water Absorption Test measures the water retention capacity of aggregates. It is essential for adjusting water content in concrete mixes, ensuring proper workability, strength, and durability in construction projects.

Coarse Aggregates Tests
Sulphate Soundness (Magnesium & Sodium)
The Sulphate Soundness Test measures the durability of coarse aggregates against chemical attacks by sulphates. It ensures aggregates resist expansion and cracking, maintaining the strength and longevity of concrete structures in construction projects.

Coarse Aggregates Tests
Material Finer Than 75 Micron
The Material Finer Than 75 Micron Test measures the proportion of fine particles in coarse aggregates passing through a 75-micron sieve. Excess fines can reduce concrete strength and workability, making this test essential for quality control and accurate concrete mix design in construction projects.
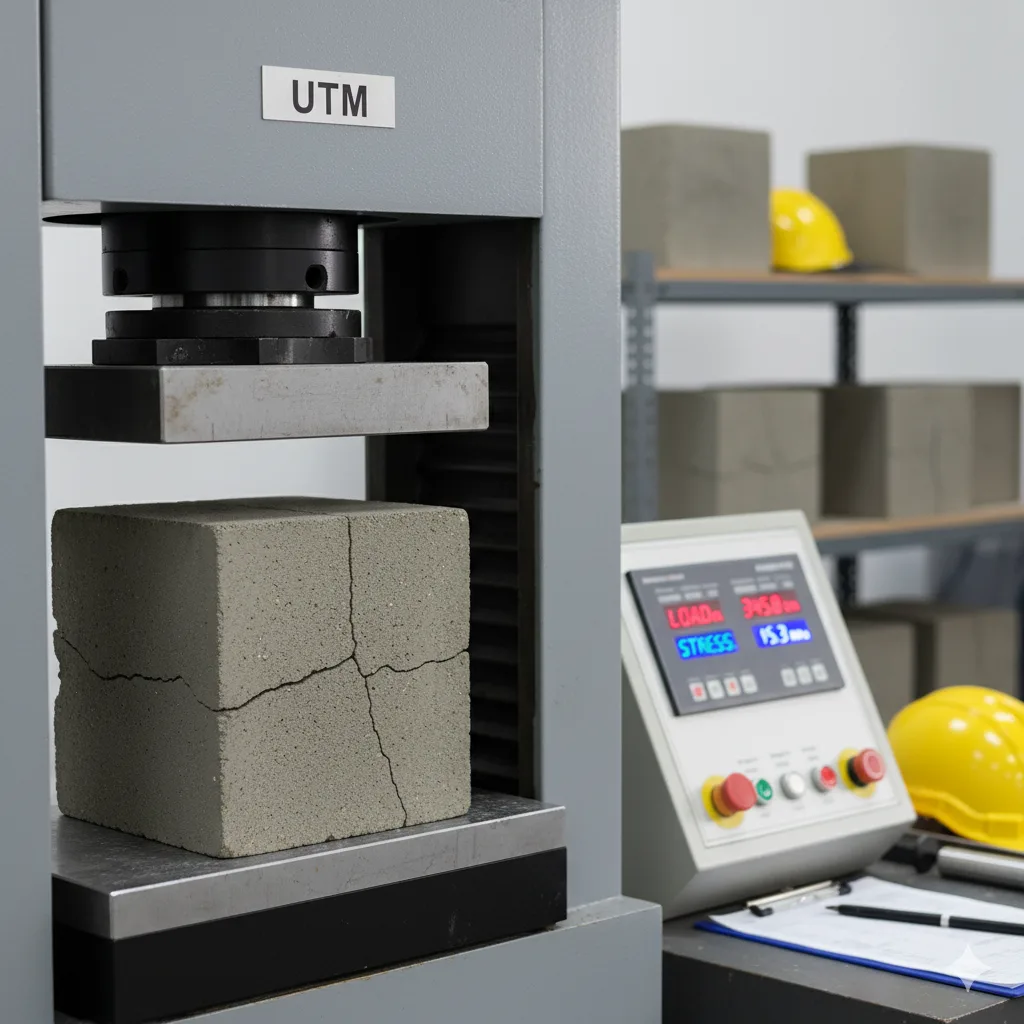

Concrete Tests
Compressive Strength of Cube
The Compressive Strength Test of Concrete Cubes measures the ability of concrete to withstand axial loads. It is essential for verifying concrete quality, ensuring durability, and confirming strength in structural elements and construction projects.
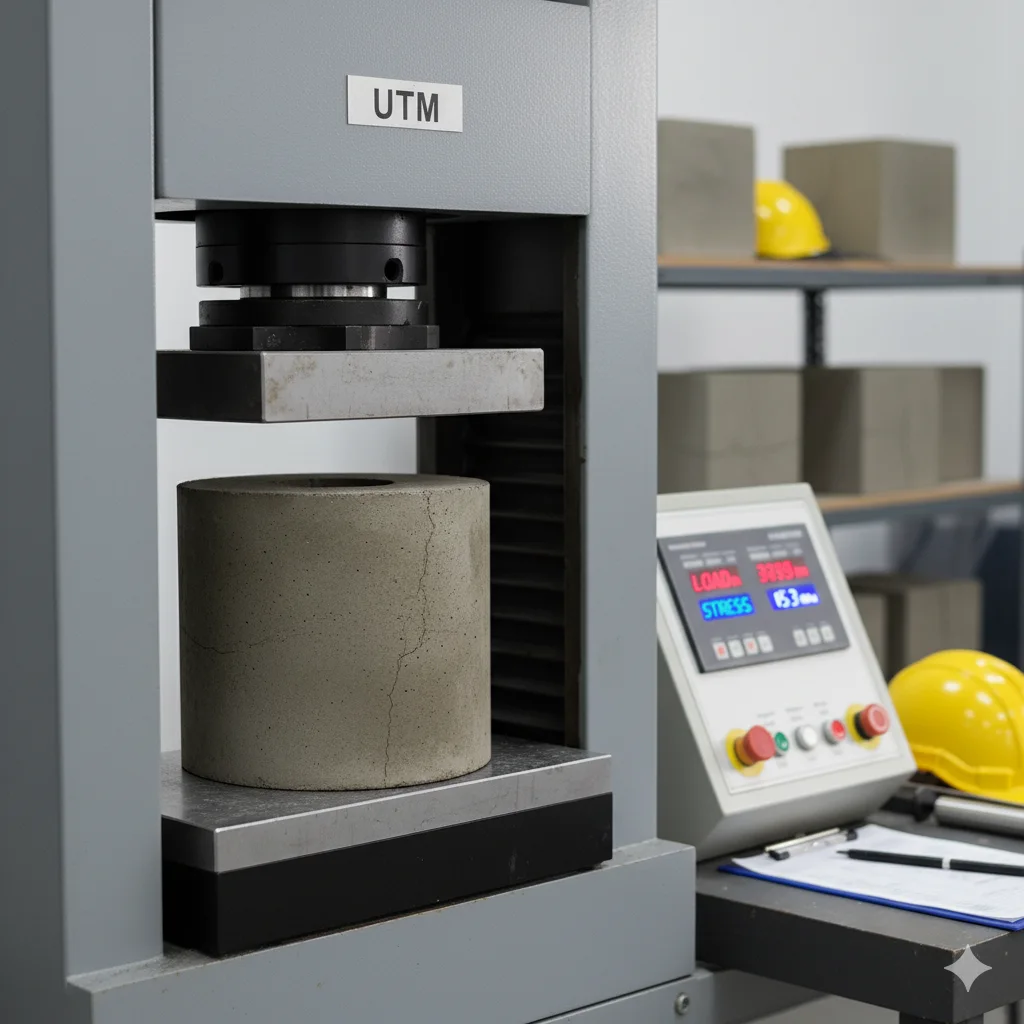

Concrete Tests
Compressive Strength of Core
Concrete Core Tests measure the compressive strength of hardened concrete taken from existing structures. They are essential for assessing in-situ concrete quality, durability, and structural performance in construction projects.
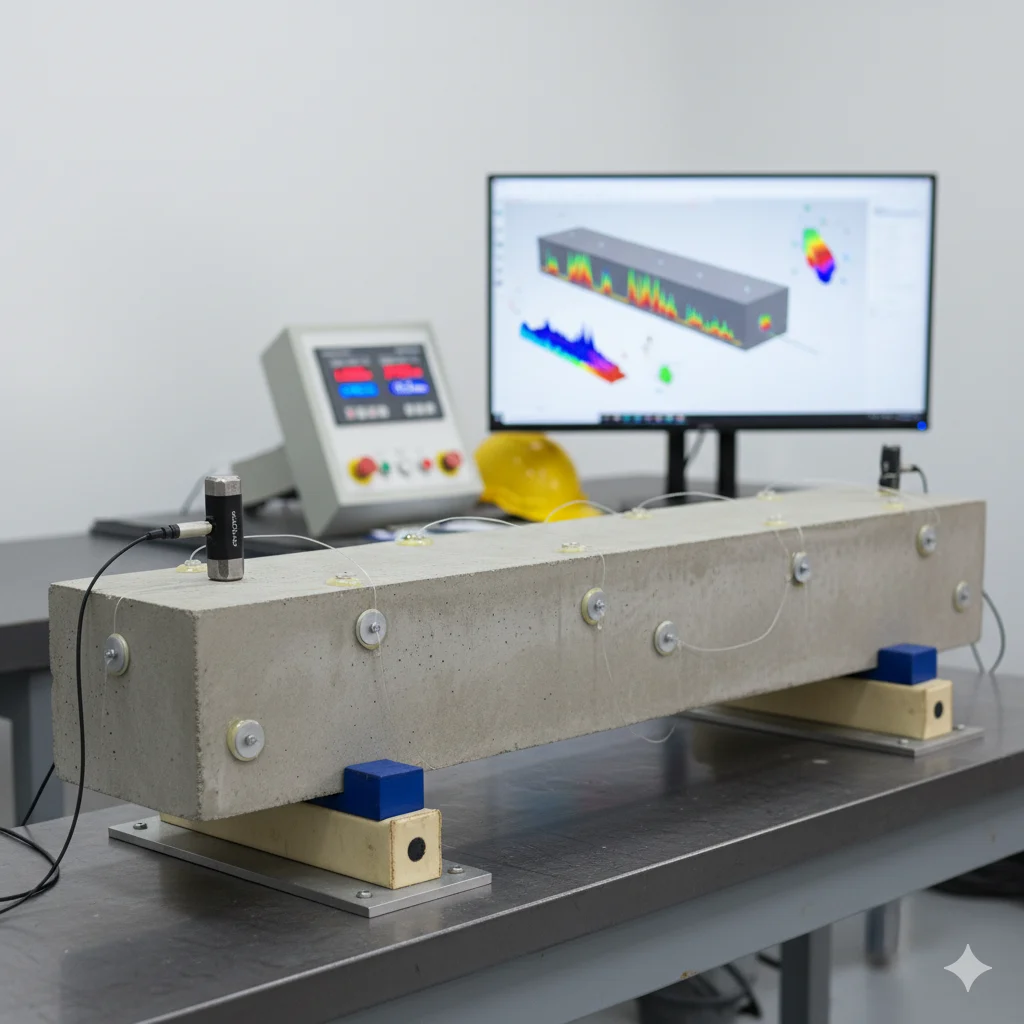

Concrete Tests
Longitudinal, Flexural & Torsional Resonance
The Non-Destructive Resonance Test measures dynamic properties of concrete, including stiffness and elasticity. It assesses structural integrity and performance without damaging the concrete, ensuring durability and safety in construction projects.
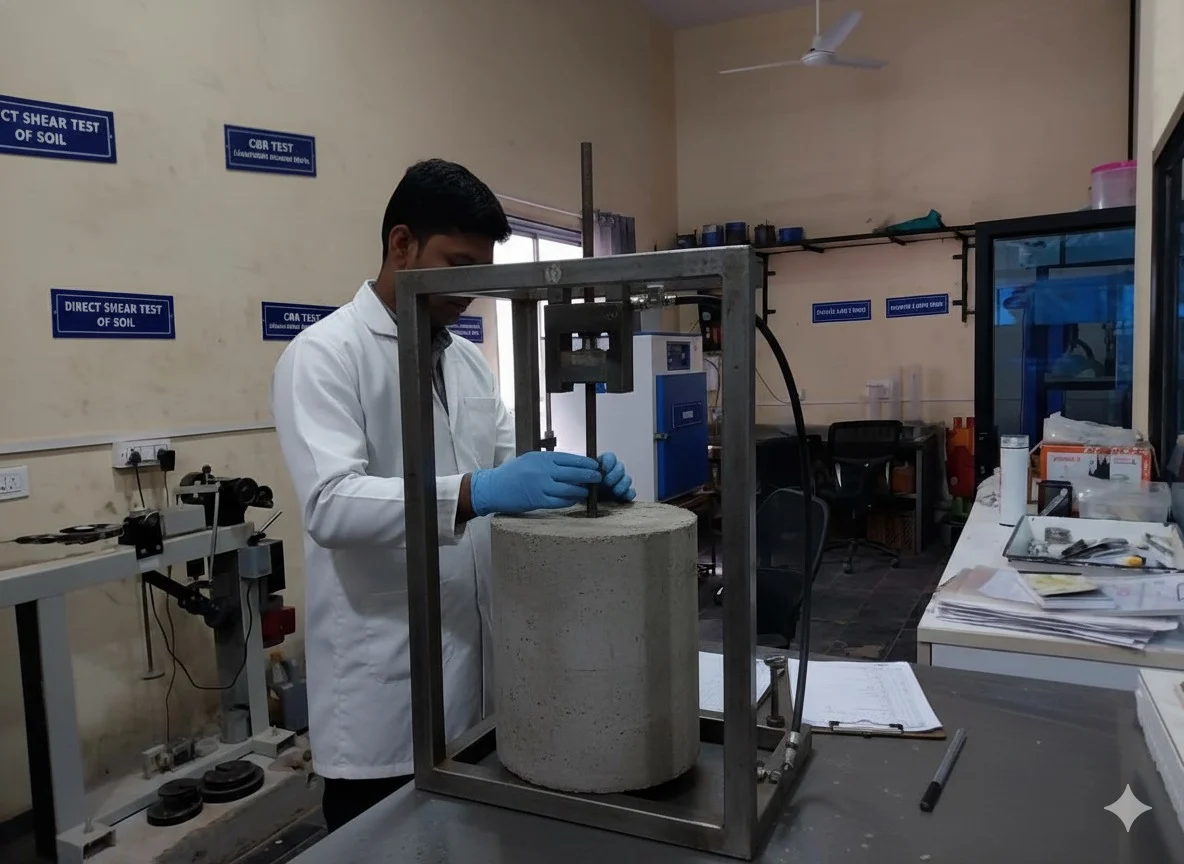

Concrete Tests
Pull Out Test - Reinforced Concrete
The Pull Out Test measures the bond strength between concrete and embedded reinforcement. It is essential for ensuring structural stability, effective load transfer, and durability of reinforced concrete in construction projects.
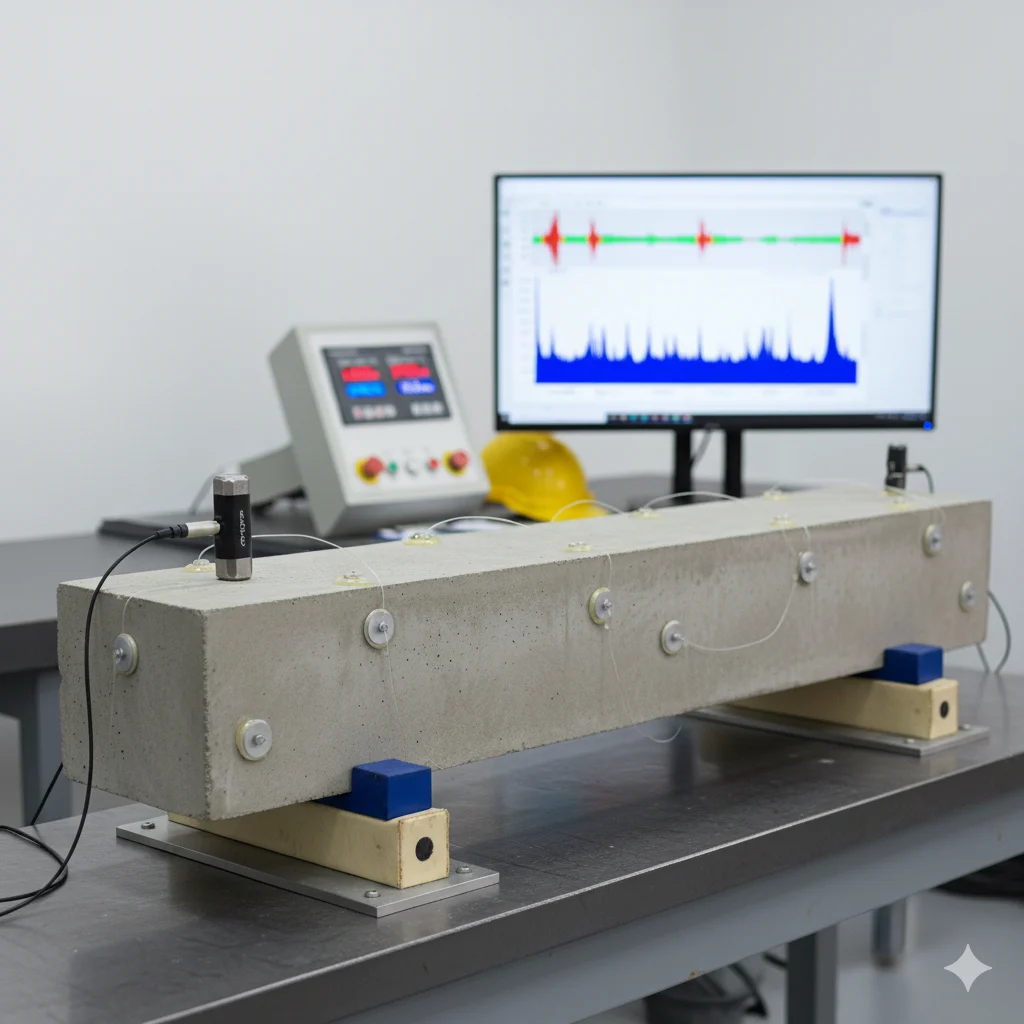
Concrete Tests
Dynamic Modulus of Elasticity
The Dynamic Modulus of Elasticity Test measures the stiffness of concrete using vibration techniques. It is essential for assessing structural performance, durability, and behavior under dynamic loads in construction projects.
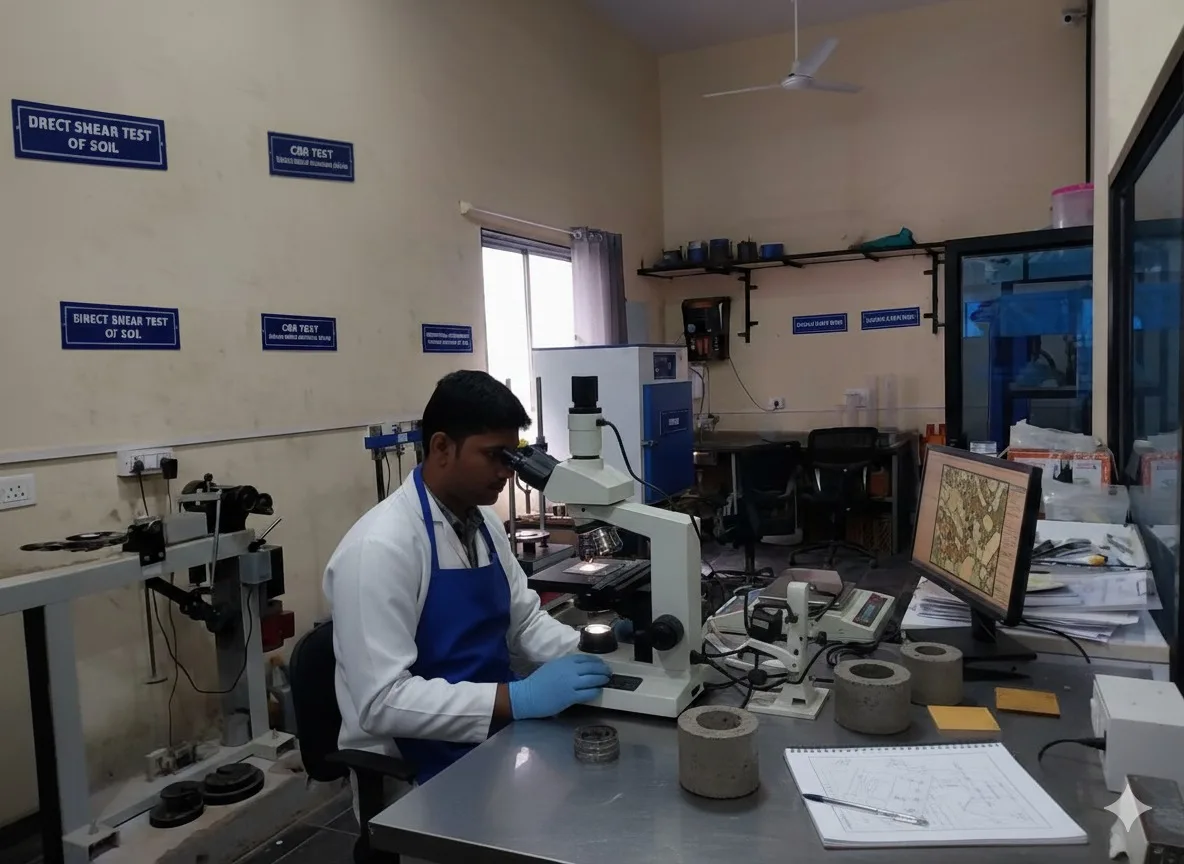

Concrete Tests
Petrographic Analysis (Concrete)
Petrographic Analysis examines the composition and microstructure of concrete to identify defects, assess durability, and detect potential failure mechanisms. It is essential for quality control and long-term performance evaluation in construction projects.
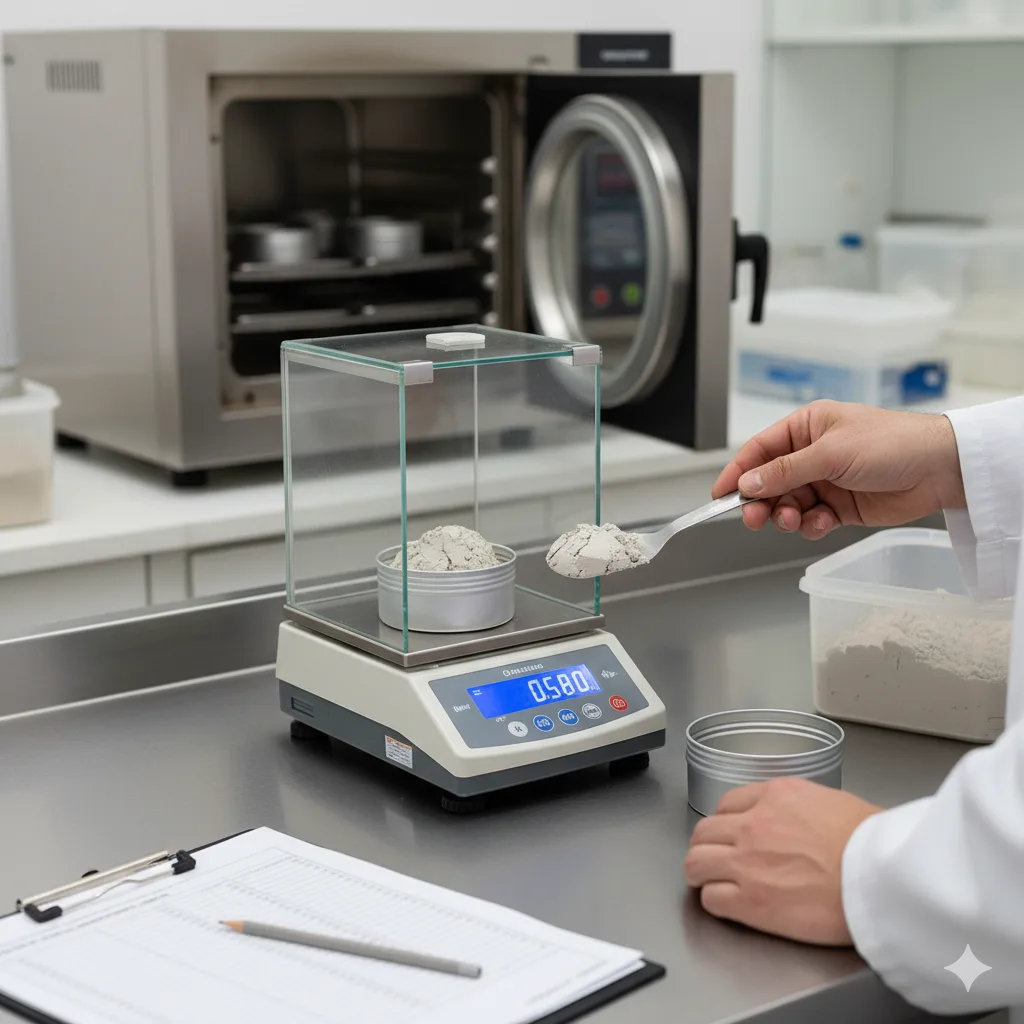

Bentonite Tests
Natural Moisture Content
The Natural Moisture Content Test measures the moisture present in bentonite. It is essential for evaluating swelling properties and determining suitability for sealing, drilling, and various industrial applications.
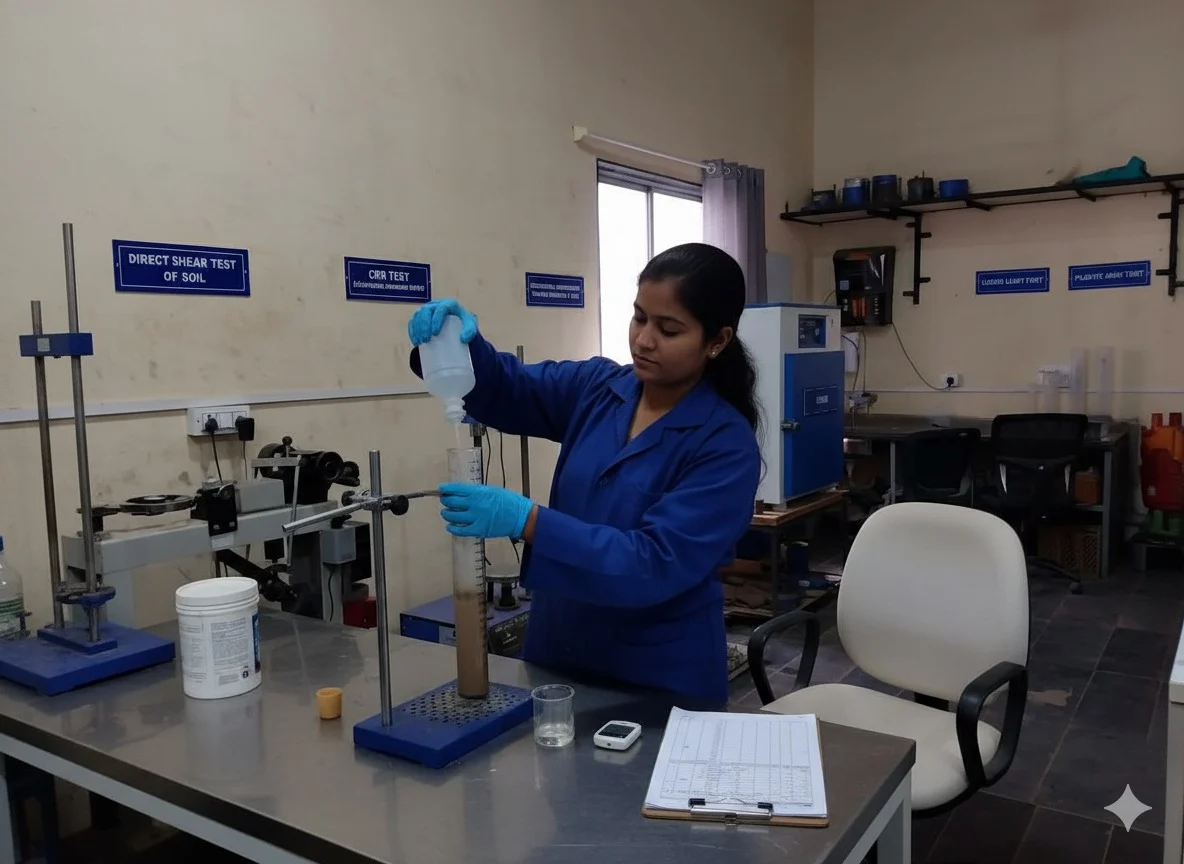

Bentonite Tests
Sand Content
The Sand Content Test measures the proportion of sand in bentonite. High sand content can reduce swelling efficiency and affect the performance of bentonite in sealing, drilling, and other industrial applications.
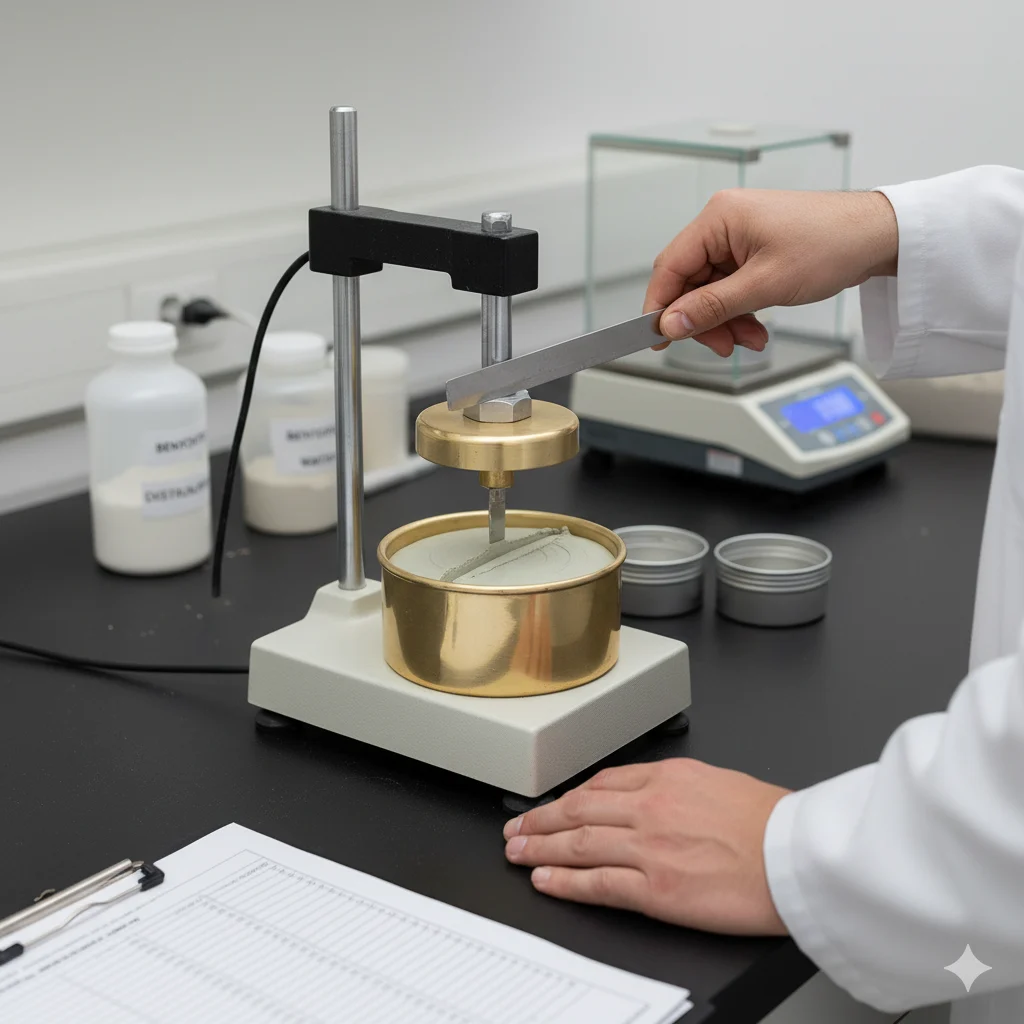

Bentonite Tests
Liquid Limit
The Liquid Limit Test determines the water content at which bentonite changes from a plastic to a liquid state. It is essential for evaluating swelling properties, compaction behavior, and suitability in sealing, drilling, and industrial applications.
